Jsfe
📝 JSON Schema Form Element
Effortless forms, with standards.
Features:
- Instant form generation based on your JSON schemas.
- Integrates within your OpenAPI / JSON schema / MongoDB (BSON) stack.
- Comes with sensible defaults, while aiming for extensibility (themes, widgets…).
- ⚡️ Fast, and light 🪶.
Use cases:
- Quick CRUDs for you backends (JS, Python, PHP, Ruby…).
- Lightly interactive websites contact forms.
- Building block for custom CMSes.
- Building block for Markdown YAML frontmatter editors.
- Form builders… builder (🪆)
- _You name it_…
Due to their declarative and serializable nature, JSON schemas are highly interoperable and portable.
Moreover, UI schemas can be declared alongside to customize the view layer.
You can also override totally one ore more widgets, or just sprinkle some styles on top of the included ones.
Why?
While there is a handful of project for major frontend frameworks, there wasn't any Web Component packing all the features above.
Also if your are evaluating Web Component design systems or if you are building your own, this library is providing you a handy testbed.
See also the inspirations for this project.
[!CAUTION]
Not for production.
Expect the doc. to be not in sync. with the actual released code.
Jump to implementations:
— Pure HTML (CDN)
— TypeScript only (DOM)
— Astro (SSR) —
— Lit
— Solid
— Vue
— Svelte
— (P)React
—
🗂️ Table of Contents
Field types
Primitives
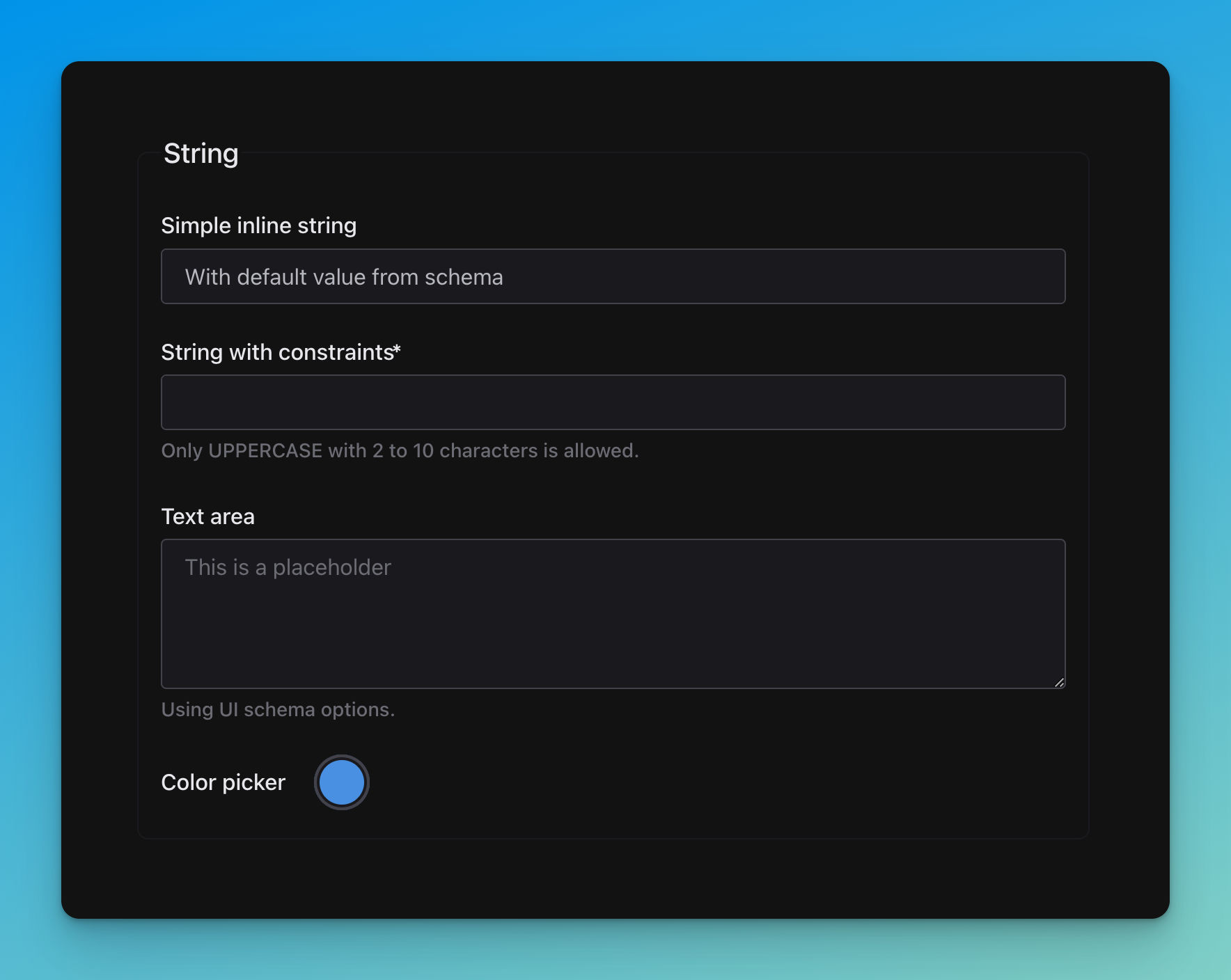
String
title: String
required:
- stringConstrained
properties:
simpleString:
title: Simple inline string
type: string
default: With default value from schema
stringConstrained:
title: String with constraints
type: string
pattern: '^[A-Z \d\W]+$'
minLength: 2
maxLength: 10
description: Only UPPERCASE with 2 to 10 characters is allowed.
textArea:
title: Text area
description: Using UI schema options.
type: string
color:
title: Color picker
type: string
default: '#4a90e2'
# UI schema
textArea:
'ui:widget': textarea
'ui:placeholder': This is a placeholder
color:
'ui:widget': color
Number
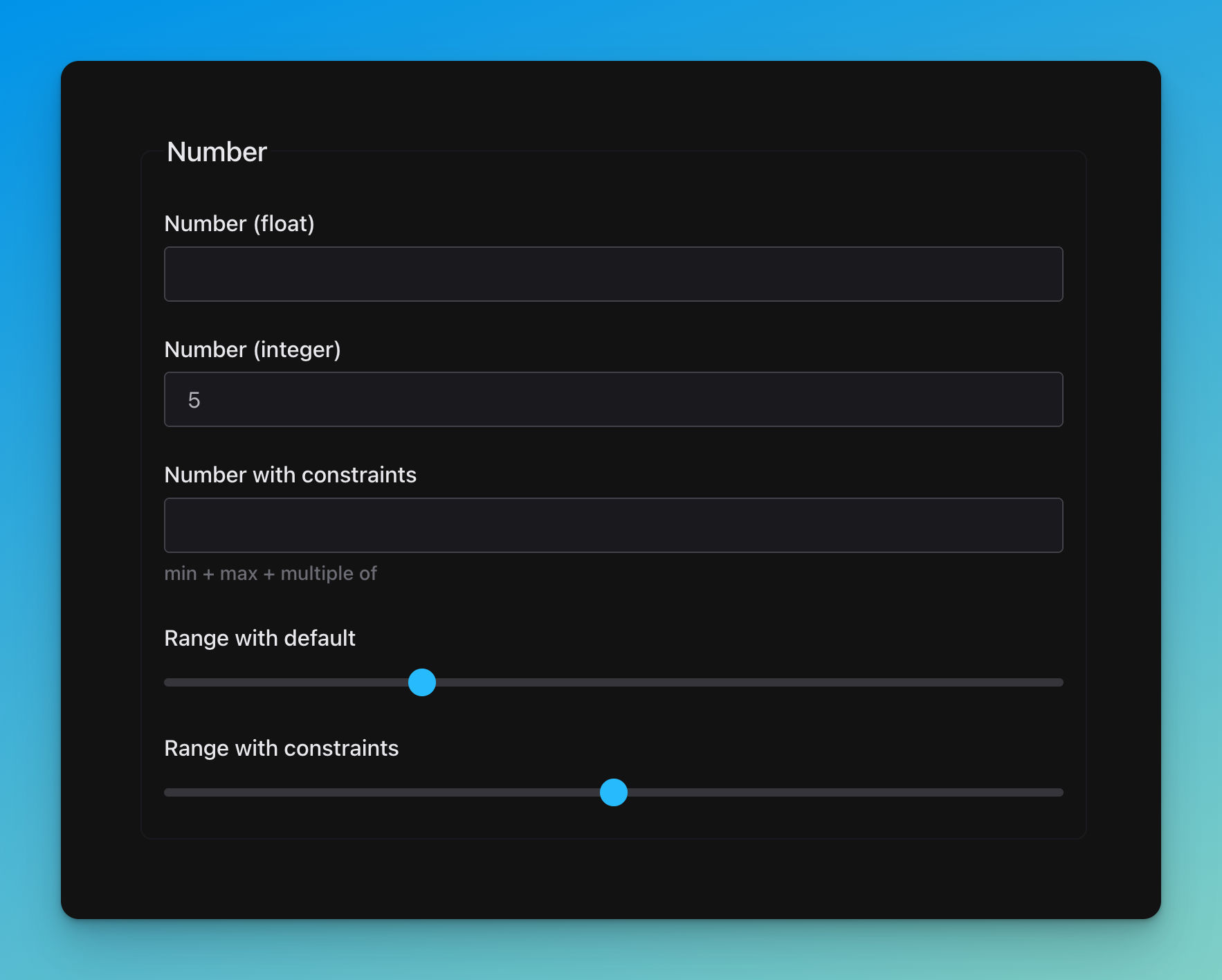
title: Number
properties:
float:
title: Number (float)
type: number
integer:
default: 5
title: Number (integer)
type: integer
numberConstrained:
title: Number with constraints
description: min + max + multiple of
type: integer
minimum: 50
maximum: 100
multipleOf: 10
range:
title: Range with default
default: 28
type: integer
rangeConstrained:
title: Range with constraints
type: integer
minimum: -50
maximum: 50
multipleOf: 25
# UI schema
range:
'ui:widget': range
rangeConstrained:
'ui:widget': range
Boolean
title: Boolean
properties:
checkbox:
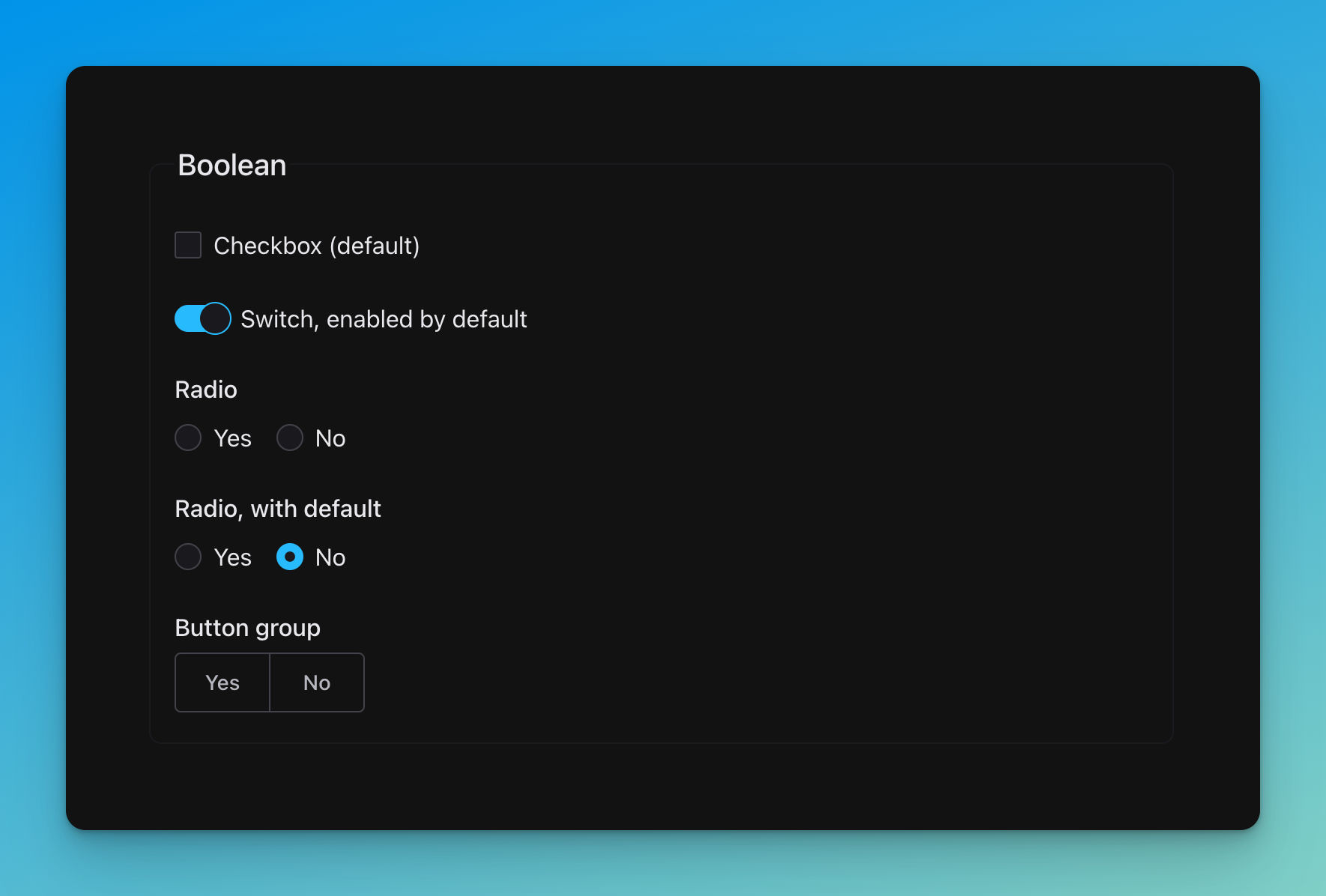
title: Checkbox (default)
type: boolean
switch:
title: 'Switch, enabled by default'
type: boolean
default: true
radio:
title: Radio
type: boolean
radioWithDefault:
title: 'Radio, with default'
type: boolean
default: false
buttonGroup:
title: Button group
type: boolean
# UI schema
switch:
'ui:widget': switch
radio:
'ui:widget': radio
radioWithDefault:
'ui:widget': radio
buttonGroup:
'ui:widget': button-group
Enumeration
title: Enumeration
properties:
select:
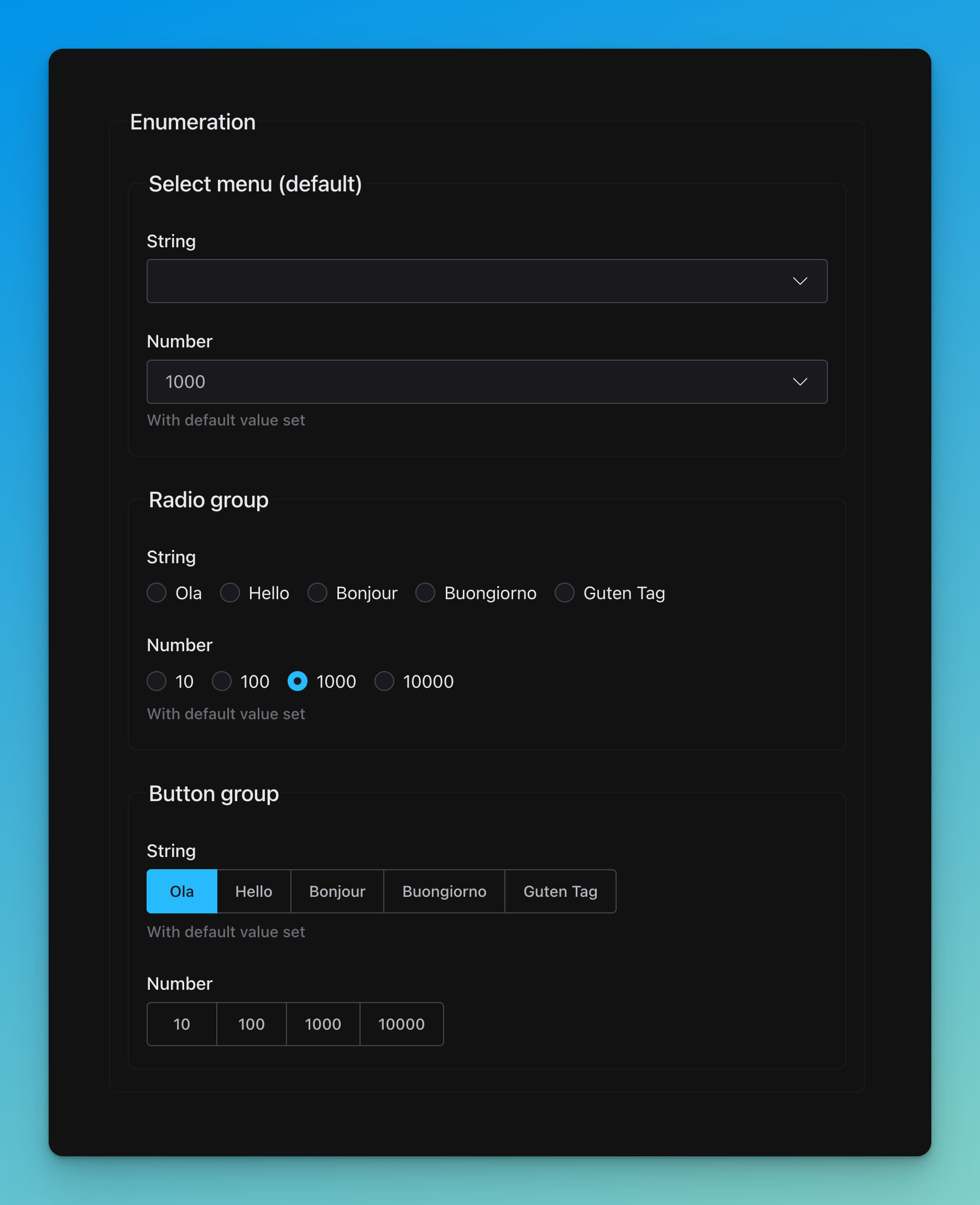
title: Select menu (default)
properties:
string:
title: String
type: string
enum: [Ola, Hello, Bonjour, Buongiorno, Guten Tag]
number:
title: Number
type: number
enum: [10, 100, 1000, 10000]
description: With default value set
default: 1000
radio:
title: Radio group
properties:
string:
title: String
type: string
enum: [Ola, Hello, Bonjour, Buongiorno, Guten Tag]
number:
title: Number
type: number
enum: [10, 100, 1000, 10000]
description: With default value set
default: 1000
buttonGroup:
title: Button group
properties:
string:
title: String
type: string
enum: [Ola, Hello, Bonjour, Buongiorno, Guten Tag]
default: Ola
description: With default value set
number:
title: Number
type: number
enum: [10, 100, 1000, 10000]
# UI schema
radio:
string:
'ui:widget': radio
number:
'ui:widget': radio
buttonGroup:
string:
'ui:widget': button-group
number:
'ui:widget': button-group
Date
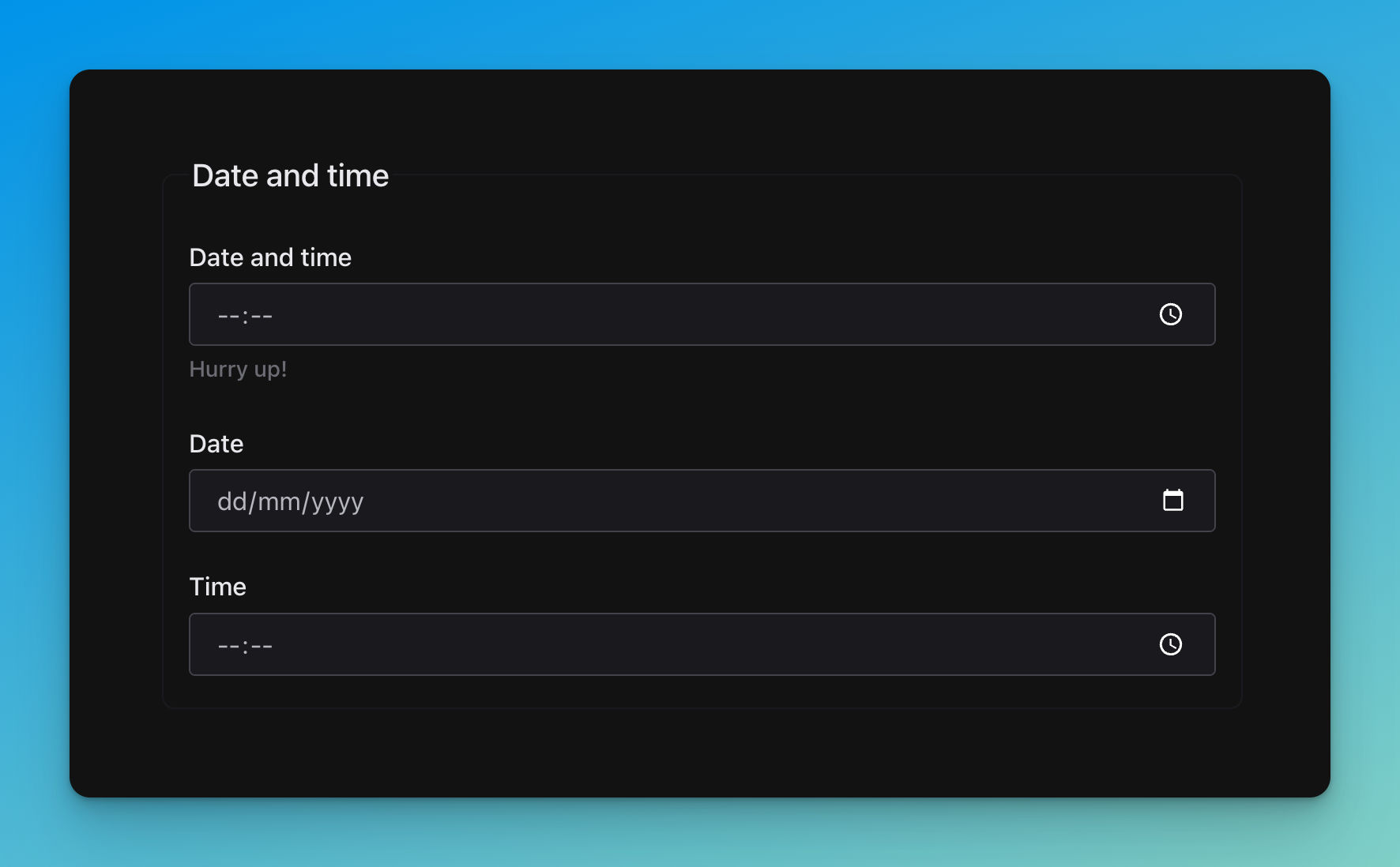
title: Date and time
properties:
datetime:
title: Date and time
description: Hurry up!
type: string
format: date-time
date:
title: Date
type: string
format: date
time:
title: Time
type: string
format: time
Object
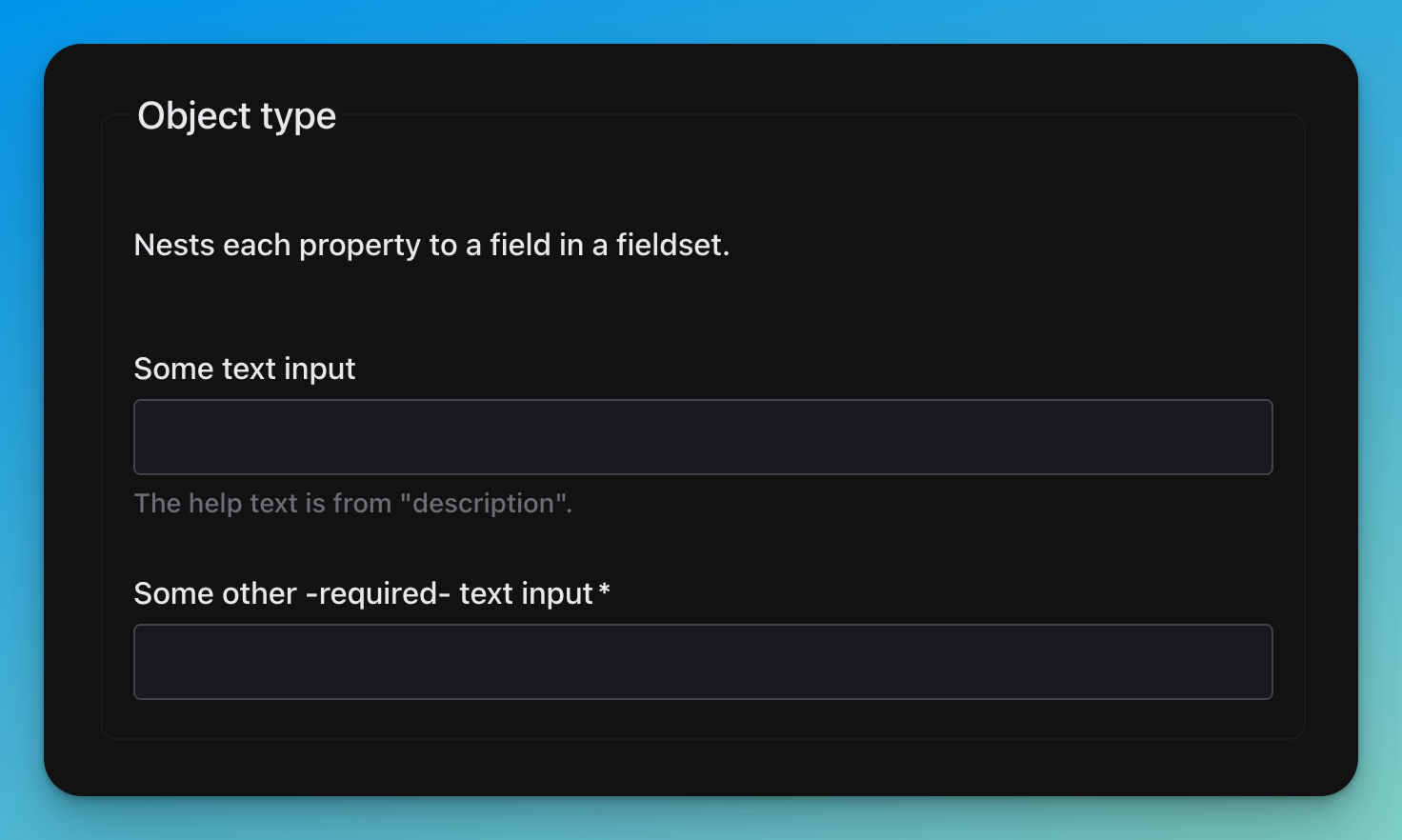
title: Object type
description: Nests each property to a field in a fieldset.
required:
- textBar
properties:
textFoo:
title: Some text input
type: string
description: The help text is from "description".
textBar:
title: Some other -required- text input
type: string
Additional properties
🚧……🚧
Arrays
Basic
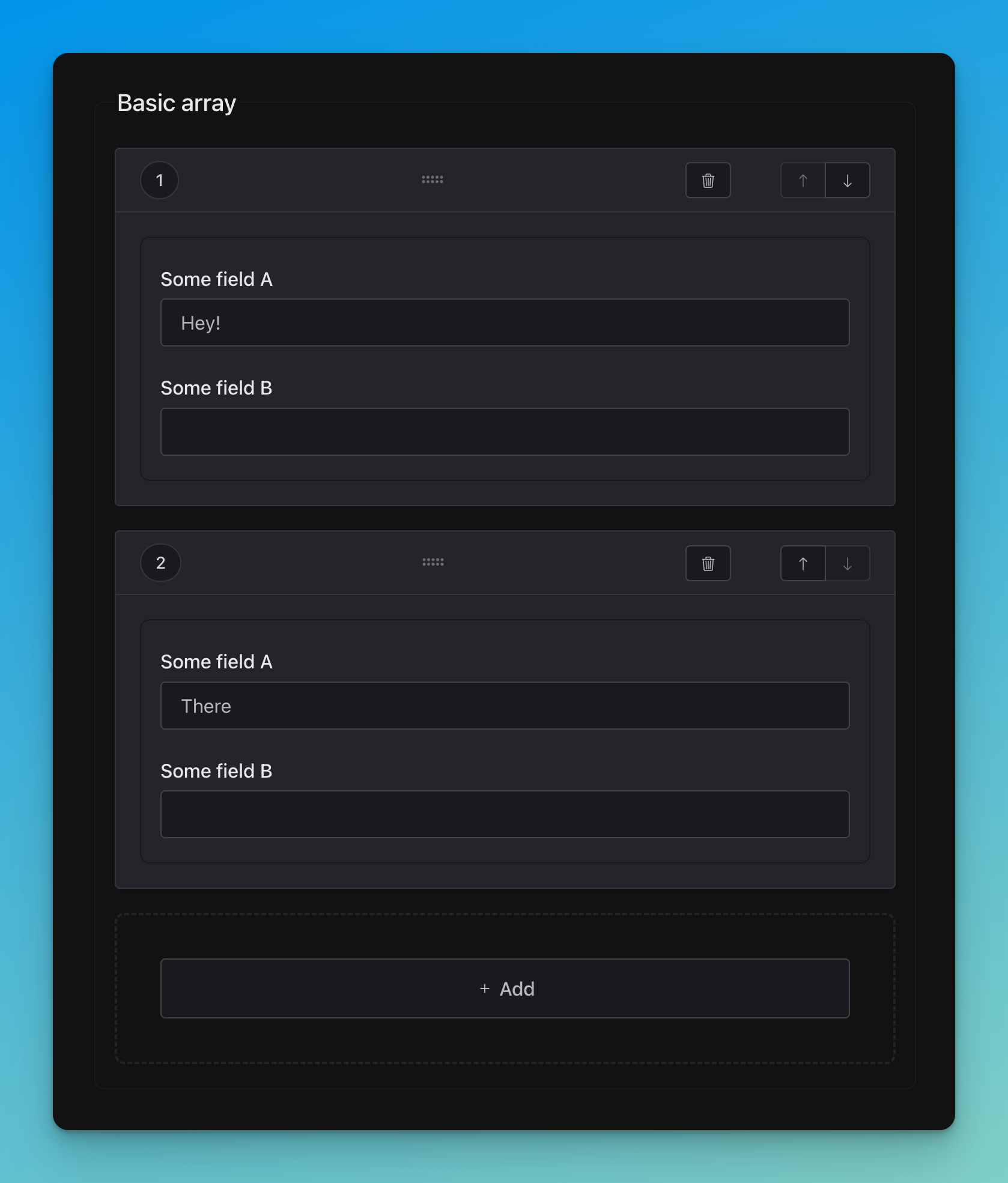
title: Basic array
type: array
items:
properties:
textA:
title: Some field A
type: string
textB:
title: Some field B
type: string
Fixed
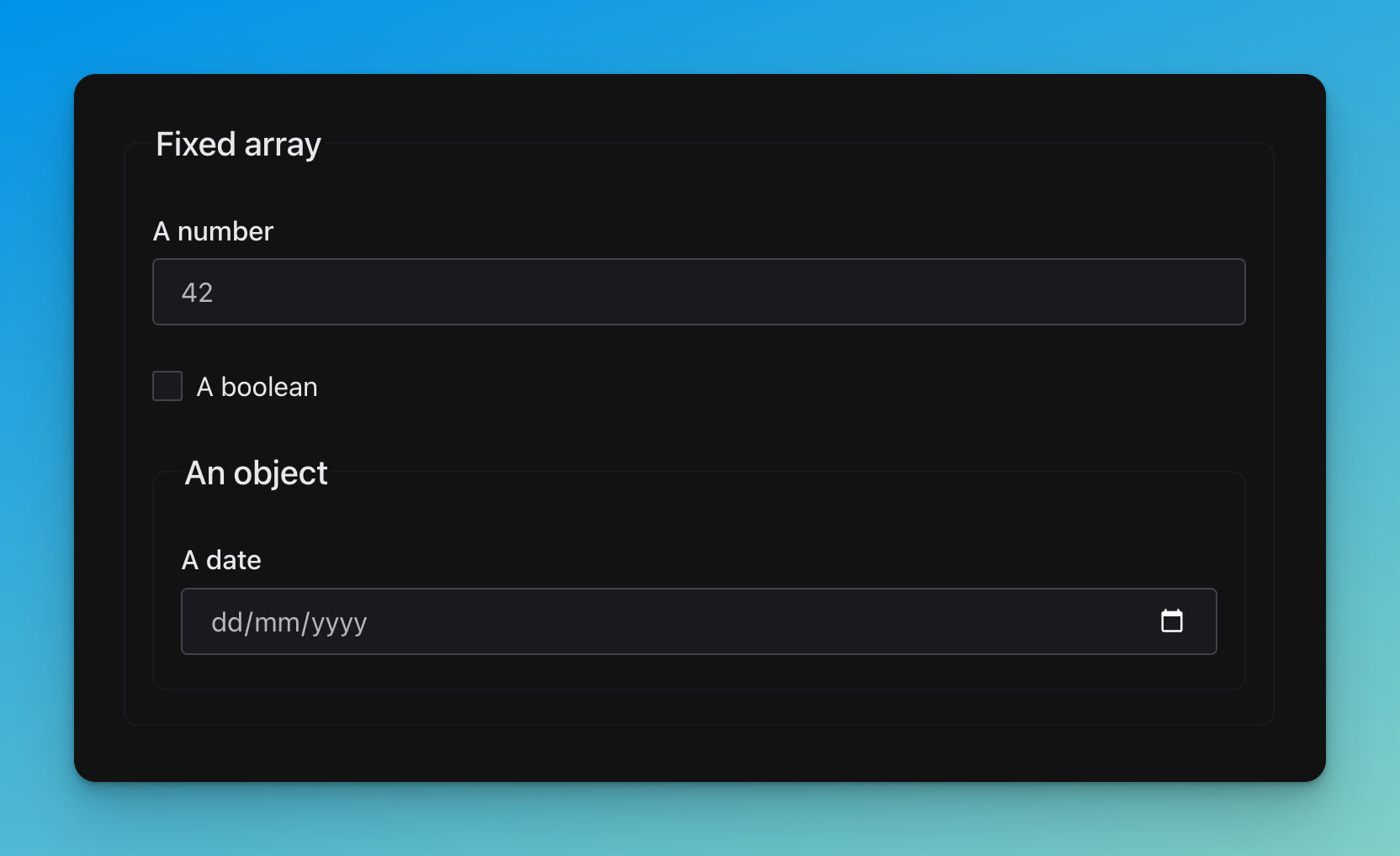
title: Fixed array
type: array
items:
- title: A number
type: number
default: 42
- title: A boolean
type: boolean
default: false
- title: An object
properties:
when:
title: A date
type: string
format: date
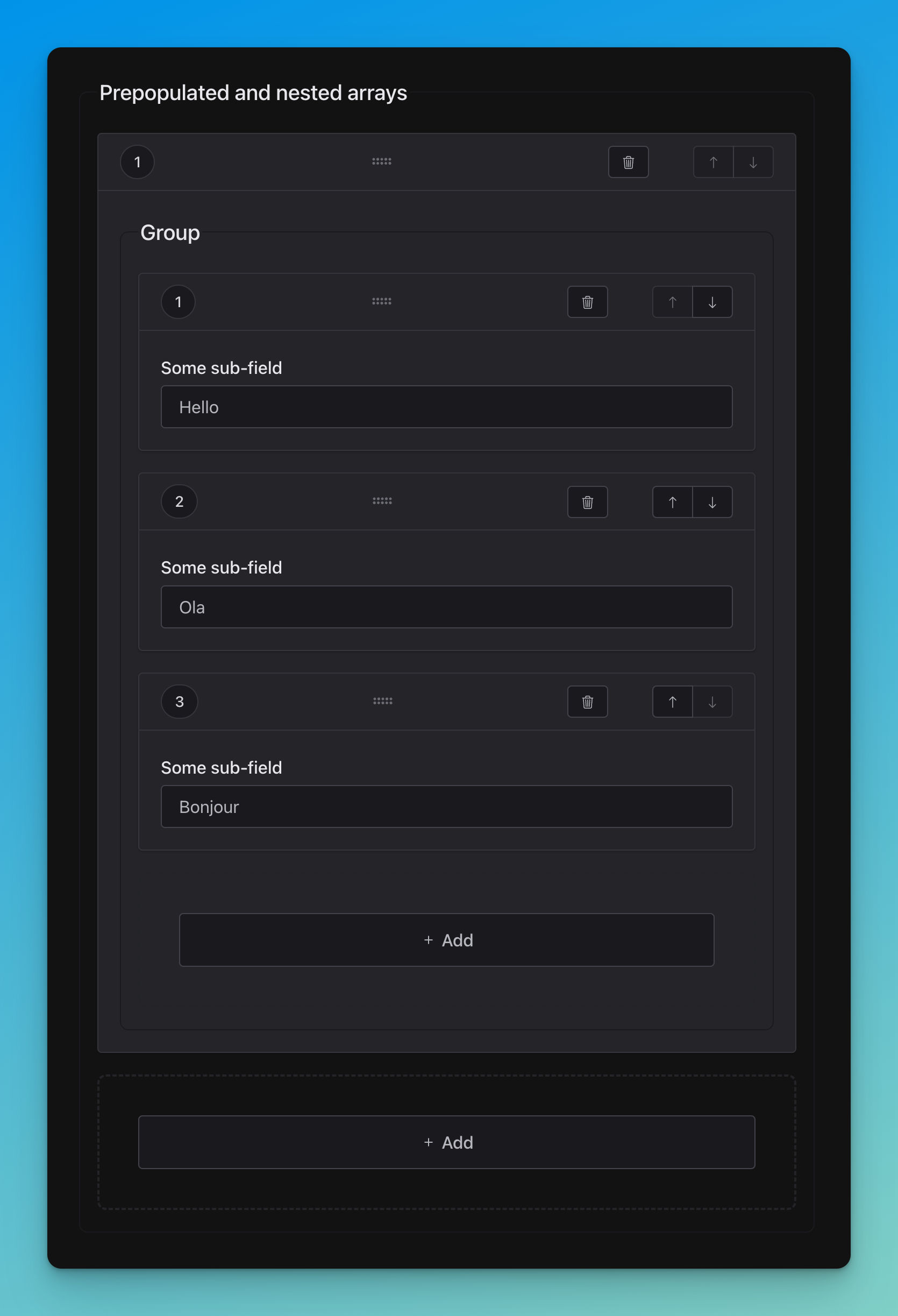
Nested
title: Prepopulated and nested arrays
type: array
items:
title: Group
type: array
items:
title: Some sub-field
type: string
# Data
prepopulatedNested:
- - Hello
- Ola
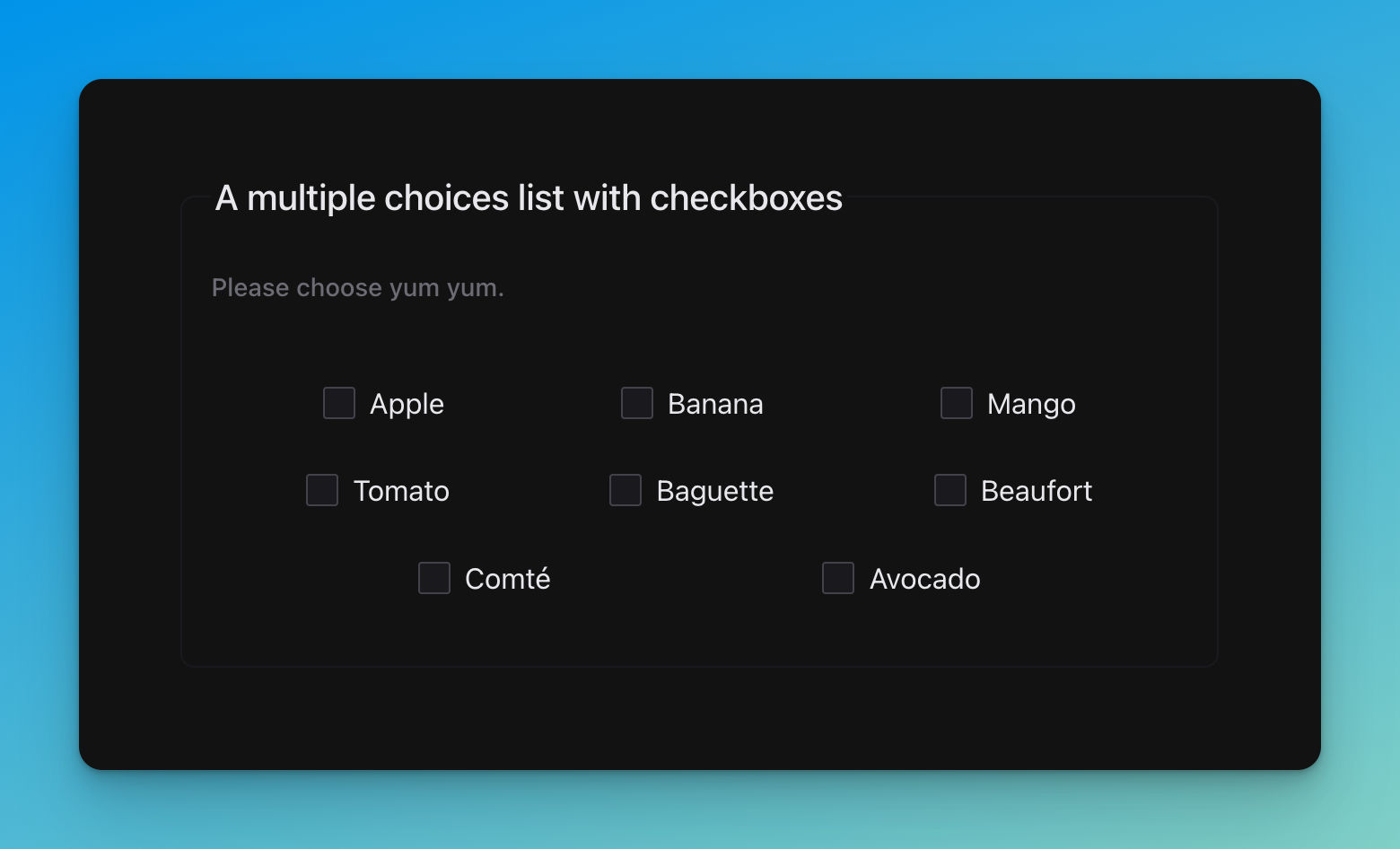
Multiple choices (enums.)
title: A multiple choices list with checkboxes
description: Please choose yum yum.
type: array
uniqueItems: true
items:
type: string
enum:
- Apple
- Banana
- Mango
- Tomato
- Baguette
- Beaufort
- Comté
- Avocado
Additional items
🚧……🚧
Subschemas
allOf
🚧……🚧
oneOf
🚧……🚧
anyOf
🚧……🚧
Conditionals
Dependencies
🚧……🚧
If, then, else
🚧……🚧
Miscellaneous
References
🚧……🚧
Recursivity
🚧……🚧
Nullable values
🚧……🚧
User Interface
Schema
🚧……🚧
Usage
Installation
This is for the bare package. You'll have to bring all the widgets yourself.
npm i @jsfe/form
# or
pnpm i @jsfe/form
# or
yarn add @jsfe/form
UI Libraries
See examples/src/pages/flavored.astro
Alternatively:
npm install @jsfe/shoelace
npm install @jsfe/material
npm install @jsfe/carbon
npm install @jsfe/wired
npm install @jsfe/system
<jsf-shoelace schema="..." uiSchema="..." data="..."></jsf-shoelace>
<jsf-material schema="..." uiSchema="..." data="..."></jsf-material>
<jsf-carbon schema="..." uiSchema="..." data="..."></jsf-carbon>
<jsf-wired schema="..." uiSchema="..." data="..."></jsf-wired>
<jsf-system schema="..." uiSchema="..." data="..."></jsf-system>
See also the CSS section.
Implementations
[!CAUTION]
This project is new, API is subject to changes
All examples
You can try the multi-frameworks examples like this:
npx degit https://github.com/json-schema-form-element/examples jsfe-examples
cd jsfe-examples
npm i
npm run dev
|
Implementation |
Working sources |
Code sandbox |
|---|---|---|
Pure HTML with CDN |
|
|
TypeScript (no framework) |
||
Astro (SSR) |
||
Lit |
||
Solid |
||
Vue |
||
Svelte |
||
React |
CSS
Nowadays, there are many different strategies for CSS loading / bundling. JSFE is embedding its own style in its shadow, but for components libraries (here Shoelace) you should act depending on your current workflow.
References:
- https://lit.dev/docs/components/styles
- https://vitejs.dev/guide/features.html#css
- https://shoelace.style/getting-started/installation#light-and-dark-theme
Shoelace is embedding styles chunks accross components, however CSS custom properties are injected globally.
TypeScript
Support for each implementation
| API | No framework | Astro (SSR) | Lit | Solid | Vue | React / Preact | Svelte |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Declarative control | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ via prop: |
✅ | ❌ | ❌ (4) |
| Declarative inference | ❌ (1) | ❌ (2) | ❌ (3) | ✅ via prop: |
❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Declarative type-checking | ❌ (1) | ❌ (2) | ✅ | ✅ via prop: |
❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Imperative control | ✅ via DOM | - | ✅ via ref |
✅ via ref |
✅ via ref |
✅ via ref |
✅ via use: |
| Imperative inference | ✅ via DOM | - | ✅ via ref |
✅ via ref |
✅ via ref |
✅ via ref |
✅ via use: |
| Imperative type-checking | ✅ via DOM | - | ✅ via ref |
✅ via ref |
✅ via ref |
✅ via ref |
✅ via use: |
- HTML language servers can't support TypeScript obviously. But IDE can leverage Custom Element metadata.
- Astro JSX namespace / LSP are not handling
HTMLElementTagNameMapor Custom Element metadata, yet. - Template literals are preventing automatic properties inference, but at least, you can't assign wrong argument types without knowing it.
- Svelte heuristics are not clear regarding attributes versus properties handling. Better be safe than sorry. Also the
use:directive is neat.
There might be changes regarding support for Web Components accross various the various UI frameworks above. Please file an issue if an info is wrong or missing.
Each implementation examples are trying to show off the most type-safe way to use JSFE, with the least trade-offs.
Using it more declaratively or imperatively is up to you, your framework ability and you coding style.
Both usages are valid and can be mixed. Typically when you want to use the schema elsewhere in your app., or
when your callbacks are getting too beefy, you'll better extract them from templates.
Generally, imperative usage get perfect TypeScript support (you just handle the class), whereas declaratively, you'll have to deal with various template languages limitations (this is an universal problem).
Component libraries
[!IMPORTANT]
Before you dive in, here is some context about Web Components libraries support with JSFE.
Whereas you are starting from scratch or you want to integrate declarative forms in
an existing project, you'll want to choose an UI library or build your own from scratch (or a mix of both).
In either case, JSFE got you covered up, as an agnostic platform for consuming
standardized form inputs widgets (see types).
Web Components technologies has a lot of traction in 2022-23, with big names
launching their own collections. As any flourishing eco-system, there are opinions.
Fortunately, most divergences happens on the CSS side. Specifically on styles consuming mechanisms.
As the initial maintainer, I decided to focus on Shoelace, while experimenting with other great options out there.
Why so?
- Keep an eye on converging practices across vendors.
- Ensure that JSFE remains not to tied with Shoelace way of things (which is already quite thin, relatively).
- Be able to swap out built-ins for custom widgets on a pinch, when needed.
- Borrow valuable ideas from others libraries and re-implement them with Shoelace bits when lacking.
[!WARNING]
I will not maintain the full spectrum of JSFE widgets, accross all libraries!
But I will do my best to provide all the hooks you need, thanks to an agnostic and type-safe API, smoothening some peculiarities.
Also, expect varying support for CSS implementations as for now, in 2023, it's just a bit too wild to keep up.
Non-exhaustive notes about what you might deal with WC components libraries' CSS:
- Carbon use pure SCSS import, with mixins. Only root element seems to be allowed for CSS vars injection (no
:hostor<body>…). - Material UI uses a JS color utility to inject CSS vars on
styleattributes, with a sophisticated color generator. - Shoelace is straightforward by giving us regular CSS files with vars I can apply on a boring class. But that also means you have to build your own color palette if you want to match your brand (it's easy).
- Spectrum use licensed fonts it seems?
- Spectrum has a tricky dependencies injection system, it took me the longest to achieve, and it's not perfect yet.
I'll not expand up furthermore on that, but if you're curious, it's you're lucky day. You can see and compare all styles implementations across UI libs in examples.
Also, I recommend that you take a peek at the playground source-code for themes wizardry.
I find little gems in all of these frameworks, for example:
- Carbon has neat rocker switchs for numbers
- Adobe kills it with colours
- Wired is fun
- Material has an innovative color themes generator
- …you'll find some others too!
I'm not an expert on each of this libs., and please note many of them are quite new / rapidly evolving.
That's why it's interesting to keep a bird-eye view from time to time.
Overall, Shoelace seems to be the most equilibrated in my eyes.
If you require top-notch support for you favourite UI lib. which is not Shoelace,
I encourage you to contribute,
like people did for the React JSON Schema Form project.
Core maintainers are working on the reference implementation, and community can add things of their interest.
If you want to enhance the lib. by bringing support for more fields, it's quite easy!
Just take a peek on the Shoelace package,
which is the canonical implementation (meaning it's the most complete, API-wise).
Then, you are welcome to make a pull request with new features, or bug fixes.
Shoelace
Shoelace is the UI component library of choice for rendering fields, and as a
general design system backbone for JSFE.
It's beautiful, aims for simplicity, is not too opinionated, while still having character.
That's why it's the very first library implemented in JSFE.
Custom widgets
Design choices
You might have noticed that JSFE is not using Custom Elements as a medium for injecting widgets.
First prototypes were using them, but I've had troubles regarding the parent form element awareness about its children.
E.g. with Shoelace, inputs weren't responding well with form validation, the ENTER key for submit, etc.
I'm sure there are ways to circumvent those hassles (forwarding events…). I tried, but for now it's not a priority, as that might affect various UI libs in different ways.
Moreover, Web Components users are eager to see Custom Registries becoming maintream. That will make the process of overriding widgets much more flexible.
For now, using Lit's TemplateResult (from a function returning a html literal) is straight-forward, however there are some trade-offs; it's a state-less function, no CSS scoping, lit-tied, etc.
Ultimately, goal is to make JSFE fully modular and agnostic, by using well-defined Custom Elements, for each individual form control.
🚧……🚧
Validation
You're responsible to hook-up additional / more advanced validation with, e.g, AJV.
HTML native validation is already quite powerful, but you might want to do
your own wizardry.
Note that client-validation is more for user experience,
while server validation is here to ensure data integrity, provide context aware round-trips…
JSON schemas are easing up the constraints enforcement for moving data around, but you'll still have to manage traditional chores.
Good news is that they give you more time to take care of business related operations, UX…
Schema massaging
Same as advanced validation handling above,
JSFE doesn't bundle, dereference, nor it is fetching remote
schemas.
Doing so would add a huge payload to the library, and you might certainly have already those tools at hand somewhere in your stack.
Only thing it does is resolving JSON references, pointing to local definitions only.
This is because implementation is relatively trivial, without much code, and that's a much needed feature for DRY-ness, recursivity…
Hopefully it's easy to bring in an full-featured parser / resolver along, like the json-schema-ref-parser.
Custom Elements Manifests
See ./custom-elements.json & ./custom-elements.md
Packages informations
With internal dependencies included, minus peer dependencies (UI libs.):
| Package | Size | Version |
|---|---|---|
| @jsfe/form |  |
|
| @jsfe/shoelace |  |
|
| @jsfe/material |  |
|
| @jsfe/carbon |  |
|
| @jsfe/wired |  |
|
| @jsfe/system |  |
|
| @jsfe/types |  |
@jsfe/form contains the base class from which all other packages extends themselves from.
You don't need to install it, unless you want to provide widgets and styles from scratch.
If you just want to override some of the flavored components, @jsfe/<theme> packages are handy starters.
@jsfe/types contains everything for assisting your own widgets authoring.
It's re-exported from every package so you don't need to install it on your own.
Next versions
[!TIP]
You can try the upcoming release from thenextbranch like this:npm i @jsfe/<package>@next.
Experimental features
To activate experimental features preview flags, just pass the experimental property.
E.g. with Lit:
html`<json-schema-form
otherProps="..."
.experimental=${{
'<flag>': true,
// ...
}}
></json-schema-form>`;
Actual features flags list:
- None
Improvements
- BYOC (bring your own components).
- Extensive and modern JSON Schema support (identify Draft 4 / 7 / 2020 subtleties).
- Nice file uploaders for the
data-urlformat. - Layout customizations
- Tests, browser based (due to the WC nature).
- Tests, tests, even more tests in the field to reveal shortcomings.
- Drag and drop: improve the initial implementation (E.g. cross-nested arrays).
- Autofocuses (for added array item, etc.)
- …
- Have an idea? Discussions are open!
Acknowledgements
The Web Component and JSON Schema communities, the Lit team, the Shoelace maintainers,…
As a workhorse for many projects of mine for a long time, I'm grateful for all the ideas RSJF creators brought.
Similar projects:
See also:
- remark-lint-frontmatter-schema: Validate your Markdown frontmatter data against a JSON schema.
- retext-case-police: Check popular names casing. Example: ⚠️
github→ ✅GitHub. - astro-openapi: An Astro toolset for building full-stack operations easily, with type-safety and documentation as first-class citizens.