
Integrate your Svelte app with smart contract
Overview
This article focuses on developing a Full-stack dApp using Svelte, Ethers.js, Solidity, and Hardhat.
What we will be building?
- A front end that allows the user to send a greeting message along with a wave to the contract owner (demo)
- Display all the greeting messages on the front-end along with the sender's address
- A contract for storing a user's greeting message and their wave
Have a look at the demo video to get the better understanding of what we'll be building.
Refer to the code located here to follow along.
The Tech Stack
- Client-side framework: Svelte
- Ethereum development environment: Hardhat
- Ethereum Web Client library: Ethers.js
Prerequisites
- Node.js environment on your local machine
- MetaMask extension in your browser
You do not need real Ether as we will be using a test network for this tutorial.
Getting Started
Clone this svelte starter template which contains all the required components and CSS properties by running the following command.
git clone https://github.com/Nazeeh21/wave-portal-svelte/tree/main/code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate
Following that, navigate into the project directory and install node_modules by running the below command.
cd wave-portal-svelte/code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/
yarn
Inside the wave-portal-starter-boilerplate directory, install ethers and hardhat by running the following command.
yarn add ethers hardhat @nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle ethereum-waffle chai @nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers
Initializing and Configuring Ethereum development environment
To compile and deploy our smart contract, let's initialize a new Ethereum development environment with Hardhat by running the command below. Before running the script, make sure we are in the wave-portal-starter-boilerplate folder.
npx hardhat
Select the following settings when prompted
- What do you want to do? .Select Create a basic sample project
- Hardhat Project Root . Press Enter to set current directory as root
- Do you want to add a .gitignore? (Y/n) . n
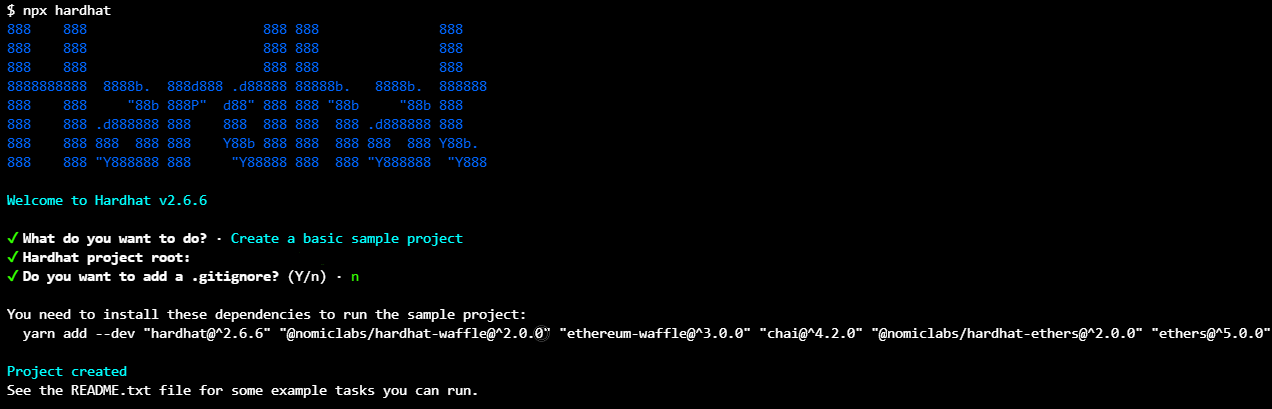
Following that, run the following command
yarn add --dev "hardhat@^2.6.6" "@nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle@^2.0.0" "ethereum-waffle@^3.0.0" "chai@^4.2.0" "@nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers@^2.0.0" "ethers@^5.0.0"
Now you should see a hardhat.config.js file. You should also have the contracts and scripts folders in your code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/ directory.
Due to a MetaMask configuration issue, we need to update the chain Id of our Hardhat Configuration to 1337. Also, we need to update the location for the artifacts to be in the code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/src directory of our app.
Navigate to code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/hardhat.config.js file. This file consists of all the configurations regarding the hardhat ethereum environment. Make sure your hardhat.config.js looks like this.
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.8.4",
paths: {
artifacts: "./src/artifacts",
},
networks: {
hardhat: {
chainId: 1337,
},
},
};
We have our Ethereum Environment ready, so let's get our smart contract.
Delete Greeter.sol under the code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/contracts folder in the root directory and create a new file named WavePortal.sol. WavePortal.sol is our smart contract for this project. In this new file, paste the smart contract from below. This contract will allow us to store the wave, reaction type, greeting message and grants prizes to a random user.
Your WavePortal.sol file should look like this.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSE
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract WavePortal {
enum Reaction {
Wave,
Cake,
Hype
}
struct Wave {
Reaction reaction;
string message;
address waver;
uint256 timestamp;
}
uint256 totalWaves;
Wave[] public waveList;
event NewWave(
Reaction reaction,
string message,
address indexed from,
uint256 timestamp
);
constructor() {}
function wave(Reaction _reaction, string memory _message) public {
totalWaves += 1;
waveList.push(Wave(_reaction, _message, msg.sender, block.timestamp));
emit NewWave(_reaction, _message, msg.sender, block.timestamp);
}
function getAllWaves() public view returns (Wave[] memory) {
return waveList;
}
function getTotalWaves() public view returns (uint256) {
return waveList.length;
}
}
Explanation of the code above:
Line 1: Specifying SPDX license type, which is an addition after Solidity ^0.6.8. Whenever the source code of a smart contract is made available to the public, these licenses can help resolve/avoid copyright issues. If you do not wish to specify any license type, you can use a special value UNLICENSED or simply skip the whole comment (it won't result in an error, just a warning).
Line 2: Declaring the solidity version.
Line 4: Starting our Contract named WavePortal.
Line 5: Declaring Reaction as enum with Wave, Cake and Hype as predefined values.
Line 11: Declaring Wave as struct containing variables reaction of type Reaction, message of type string, waver of type address and timestamp of type uint.
Line 18: Declaring variable totalWaves of type uint to store the total number of waves.
Line 19: Declaring an array wavelist of type of Wave to store all the waves.
Line 21: Declaring an event NewWave, containing information about the reaction, message, sender address and timestamp of the wave. This event gets emitted once our wave gets store in the contract successfully.
Line 28: Initializing this constructor, but do not need to set anything so leaving that empty.
Line 30: Declaring function wave with two arguments, _reaction of type Reaction which will store our reaction information and _message of type string which will store the message of the user. Declaring _message as memory means, it will get destroyed from the memory once the function gets executed.
Line 36: Declaring function getAllWaves, that returns all the an array containing all the waves.
Line 40: Declaring function getTotalWaves, that returns the number of waves.
Interacting with the Ethereum blockchain
We can interact with our smart contract from our Svelte app using the combination of our contract's ABI, the Ethers.js library, and our contract address.
ABI stands for Application Binary Interface. We can think of ABI as an interface that provides our frontend with all the available callable functions and variables from our smart contract.
We can get ABIs by compiling our smart contract using a development framework like Hardhat. You can often find the ABI for a smart contract on Etherscan.
So, let us compile our smart contract by running the command below.
npx hardhat compile
On successful compiling, you should see a new folder named artifacts under the code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/src folder. You can see the ABI of our contract under artifacts/contracts/WavePortal.json folder. We can use this ABI by simply importing this .json file.
Deploying to localhost
For easy and fast interaction, we will be deploying our contract to a local test node. For that, we need to start a local chain by running the following command
npx hardhat node
Running this command will list all the accounts and their private keys in your terminal.
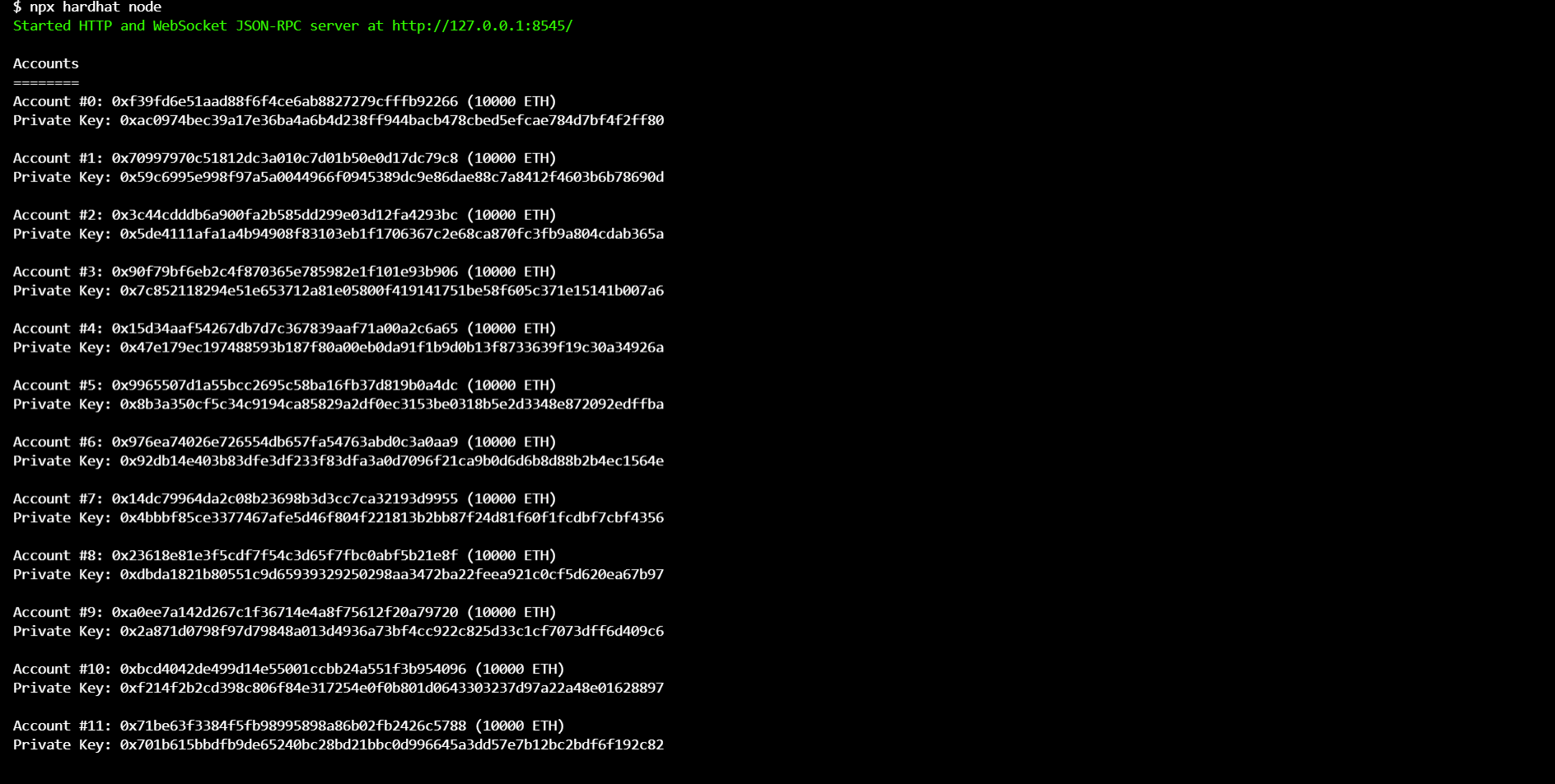
These are the 20 test accounts created for us by Hardhat that we can use to deploy and test our smart contract locally. Each account has a sufficient amount of test Ether.
Let us deploy our smart contract to localhost using one of these accounts. But before that, navigate to the code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/scripts folder and rename scripts/sample-script.js to scripts/deploy.js. This file will get executed when we'll try to deploy our contract. Inside this deploy.js file, update your main() function such that your deploy.js file looks like below.
// deploy.js
async function main() {
const WavePortal = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("WavePortal");
const wavePortal = await WavePortal.deploy();
await wavePortal.deployed();
console.log("WavePortal deployed to:", wavePortal.address);
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Explanation of the code above
Line 1: Declaring an asynchronous function main, that executes when we will deploy our smart contract.
Line 2: Calling hre.ethers.getContactFactory that returns an instance of the contract.
Line 3: Calling .deploy(), that deploys an instance of the contract
Line 4: Calling .deployed(), that awaits for the contract to get deployed.
Line 5: Logging the address of the deployed contract in the console.
Line 7: Calling the main() function and add error handling.
Now, let us run the deploy script and provide the flag --network localhost to the CLI which indicates that we want to deploy to our local network.
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network localhost
This script will deploy our smart contract to our local network and now we should be able to interact with it.
On successful deployment, you should see the following output in your terminal

This contract is deployed on the local node, using the first account that was created when we started the local network.
Store this address for your reference, as we will need it while interacting with our smart contract from our Svelte Client.
Now, to send a transaction to our smart contract deployed on the test node, we need to configure MetaMask wallet to use one of the accounts created by hardhat while running the command npx hardhat node
Let us import one of these accounts into our MetaMask wallet and use its test ethers. To do so, open MetaMask and update the network to be Localhost 8545
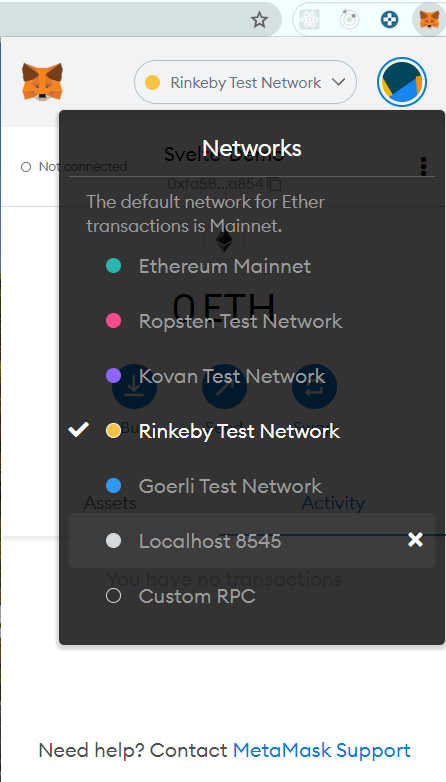
On Localhost 8545, click on Import Account from the accounts menu on the top-right.
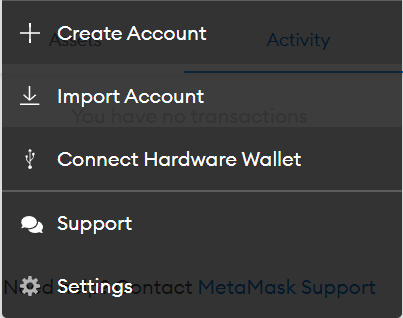
Copy and paste any one of the private keys from the CLI and click on Import. Once the account is imported, you should see the MetaMask interface like this.
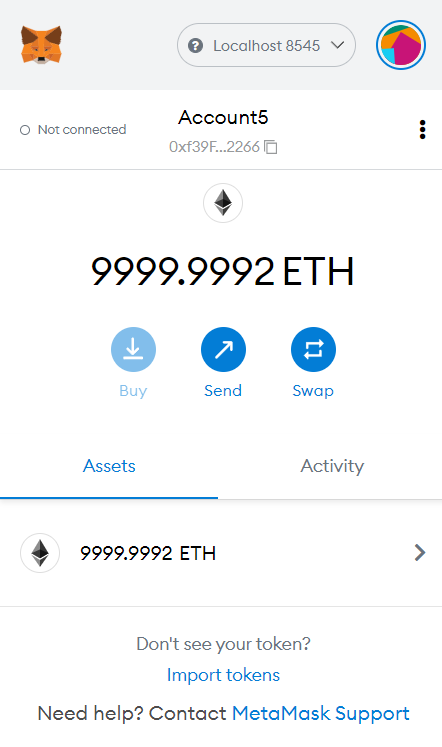
As we have our contract deployed and our MetaMask wallet configured, let us start interacting from our Svelte frontend.
Connecting with Svelte Client
For this tutorial, we are not going to focus on developing the UI, instead, we will be focussing entirely on the core functionality and integration. In the frontend, we will mainly focus on 2 things
- Fetch all the greeting messages from our smart contract and display them in the frontend.
- Create functions to send messages along with the greeting.
Let us start integration with our front end. To test our frontend, start the server using the following command.
Before starting the server, make sure that the current directory is
code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/
yarn dev
Now you should see our front end as below on the localhost:5000. If localhost:5000 doesn't work then try http://127.0.0.1:5000/.
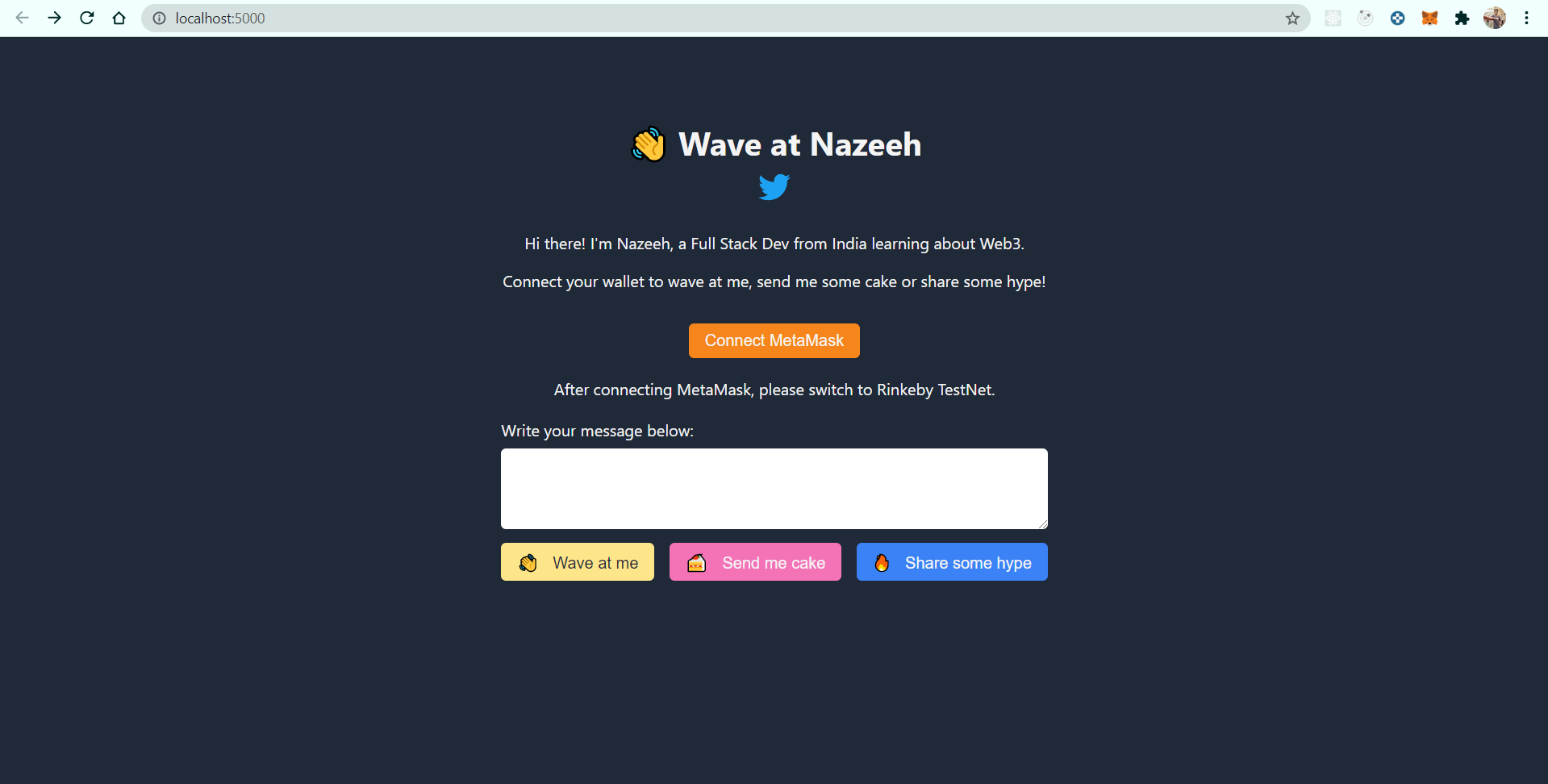
You will notice that, by clicking on any of the greetings, nothing is happening. Also, we are not able to see any previous greetings. So, let us add logic to send greetings to our smart contract and fetch all the previous greetings.
Navigate to the App.svelte file under the code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/src folder. App.svelte gets rendered on the home page upon server start and thus contains all the functionality to fetch the waves.
Update your contract address on line 10, which logged into the CLI while deploying it.
const CONTRACT_ADDRESS = 'YOUR_CONTACT_ADDRESS';
Now, paste the below code in the getAllWaves() function on line 12 in App.svelte. This function fetches all the greetings from the blockchain network to our Client.
async function getAllWaves() {
if (!window.ethereum) {
return;
}
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(window.ethereum);
const wavePortalContract = new ethers.Contract(
CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
WavePortal.abi,
provider
);
const recievedWaves = await wavePortalContract.getAllWaves();
if (!recievedWaves) {
waveList = [];
return;
}
const normalizeWave = (wave) => ({
reaction: wave.reaction,
message: wave.message,
waver: wave.waver,
timestamp: new Date(wave.timestamp * 1000),
});
waveList = recievedWaves
.map(normalizeWave)
.sort((a, b) => b.timestamp - a.timestamp);
console.log('waveList: ', waveList);
return;
}
Explanation of the code above
Line 1: Declaring an asynchronous function getAllWaves() that will fetch all the waves from our smart contract.
Line 2: Checking if we are getting an ethereum object in our window, if not we will return null.
Line 6: Getting the provider to access the blockchain data.
Line 7: Creating a local instance of our contract by passing Contract address, Contract abi and provider as an argument.
Line 12: Fetching all the waves from our smart contract by calling getAllWaves() method.
Line 13: If we do not get any waves, then we will return an empty array.
Line 18: Declaring function normalizeWave(), that will destruct the wave.
Line 25: Destructing the recievedWaves(), sorting on the basis of timestamp and assigning these sorted waves to the waveList variable.
We have to import the ABI of our WavePortal contract which enables us to interact with our smart contract. Thus add the following import statements on line 3 in App.svelte.
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
import WavePortal from './artifacts/contracts/WavePortal.sol/WavePortal.json'
Now, start the development server of svelte. You should see an error as shown below.
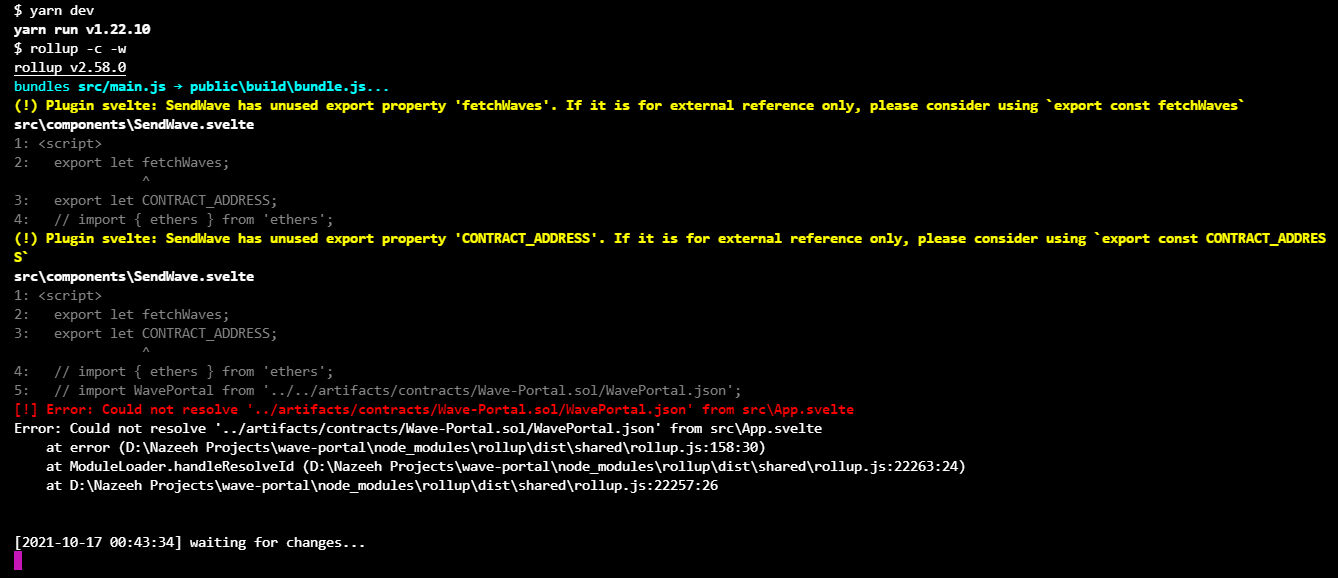
This is because we are trying to import a json file in our App.svelte and to import a json we need to add an extra plugin rollup-plugin by running the following command.
yarn add @rollup/plugin-json
Navigate to the rollup.config.js file in code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/ directory. This file contains all your configurations for the rollup. Now, in your rollup.config.js file navigate to the plugins array as show below and add json(), on line 60.
plugins: [
commonjs(),
json(),
...
]
In rollup.config.js file, in code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/ directory in order to use json(), we also need to import json() from our newly added plugin, thus add the following import statement in line 7 of rollup.config.js file.
import json from "@rollup/plugin-json";
Now, restart the development server, you should see the frontend server started successfully. Currently, you won't see any greetings on our front end because we don't have one. So, let's add a function to send the greeting.
For that, navigate to code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/src/components/SendWave.svelte file. This file will contain logic for sending the wave. Complete the sendWaveReaction() function in line 7 by pasting the code from below. This function will send wave reaction.
async function sendWaveReaction(reaction, message) {
loading = true;
try {
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(window.ethereum);
const signer = provider.getSigner();
const wavePortalContract = new ethers.Contract(
CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
WavePortal.abi,
signer
);
const transaction = await wavePortalContract.wave(reaction, message, {
gasLimit: 400000,
});
await transaction.wait();
message = '';
fetchWaves();
loading = false;
} catch (error) {
alert('Error while sending wave', error);
loading = false;
}
}
Explanation of the code above
Line 1: Declaring an asynchronous function sendWaveReaction(), that will send our reaction to our smart contract on the blockchain network.
Line 2: Setting loading variable to true.
Line 4: Declaring a provider variable that contains the read-only abstraction to access the blockchain data.
Line 5: Storing the signer object from our provider in singer variable, that will allow us to sign the transaction.
Line 6: Creating the local instance of our smart contract.
Line 11: Calling the wave() function from our smart contract, with reaction and message as an arguments.
Line 14: Waiting for the transaction to get completed.
Line 15: Resetting the value of message variable after sending the wave.
Line 16: Fetching all the waves again.
Line 17: Setting the loading indicator to false.
Line 19: Showing an alert if something goes wrong.
We also need to add the following import statements in SendWave.svelte file in line 2.
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
import WavePortal from '../artifacts/contracts/WavePortal.sol/WavePortal.json';
To interact with our smart contract from our front end, we need to connect our MetaMask wallet to our website. For that, in code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/src/components/Wallet.svelte file, complete the connectWallet() function in line 6 by pasting the below code. Wallet.svelte will contain all the logic required for connecting MetaMask wallet to our frontend.
async function connectWallet() {
walletConnected = false;
const { ethereum } = window;
await ethereum
.request({ method: 'eth_requestAccounts' })
.then((accountList) => {
const [firstAccount] = accountList;
account = firstAccount;
walletConnected = true;
})
.catch((error) => {
walletConnected = false;
connectWalletError = error;
console.log('error connecting wallet');
});
}
Explanation of the above code
Line 1: Declaring an asynchronous function connectWallet().
Line 2: Setting walletConnected variable to false.
Line 3: Getthing an ethereum object from our window.
Line 4: Calling ethereum.request({ method: 'eth_requestAccounts' }) that will give us the accounts of the connected wallet.
Line 7: Getting first account from an array of all the accounts
Line 8: Assining account variable the value of first account.
Line 9: Setting walletConnected variable to true.
Line 12: Setting walletConnected variable to false, if encountered an error while connecting wallet.
Now, restart the server if needed and you should see a MetaMask popup on clicking the Connect MetaMask button. After connecting we'll be able to successfully send greetings, waves as well as fetch all the greetings.
Now, we have our smart contract running successfully on a local node, so let's deploy it on live TestNet.
Deploying to Ropsten TestNet
We'll be deploying to the Ropsten test network in this tutorial. For that, update your MetaMask wallet to connect to the Ropsten network and send yourself some test ethers from this test faucet.
We can get access to Ropsten by signing up with a service like Infura or Alchemy. (For this tutorial I've used Infura)
Once you've created the app in Infura, you'll get a URL to a node that looks like this
https://ropsten.infura.io/v3/your_project_id
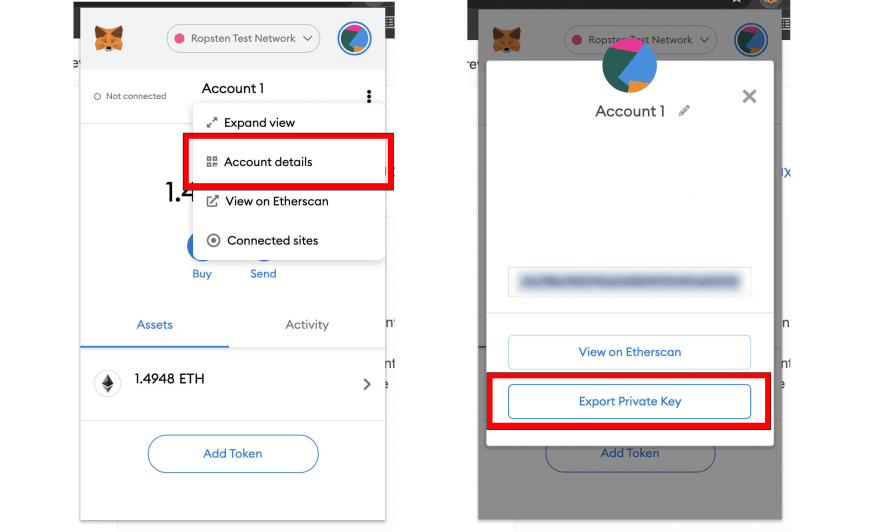
To deploy to the test network we need to update our hardhat config with a piece of additional network information. One thing is to set the private key of the wallet we'll be deploying from. You can export your private key from MetaMask by clicking menu > Account details > Export private key.
Now add networks property in hardhat.config.js in line 24 under code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/ directory as shown below.
module.exports = {
defaultNetwork: "hardhat",
paths: {
artifacts: './src/artifacts',
},
networks: {
hardhat: {},
ropsten: {
url: "https://ropsten.infura.io/v3/your_project_id,
accounts: [`0x${your-private-key}`]
}
},
solidity: "0.8.4",
};
To deploy our smart contract to the Ropsten network, run the following command in code/wave-portal-starter-boilerplate/ directory.
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network ropsten
On successful deployment, you should see the following output in your terminal.
WavePortal deployed to: 0x4f5F98f3696e1dDc107fd786d252D6Ff8D351B6b
Once your contract is deployed you should be able to start interacting with it. Now you should be able to view your live Contract on Etherscan TestNet Explorer.
What next?
A lot of things can still be improved in this project.
Try
- showing the loading indicator while the transaction is in progress
- detect the current network of the MetaMask
- if the user is on a network other than Ropsten, then prompt the user to change the network.
Congratulations! You have integrated your first dApp using Svelte. Try the challenges mentioned above and feel free to connect with me if you encounter any errors.