8mb.local
8mb.local – Self‑Hosted GPU Video Compressor
8mb.local is a self‑hosted, fire‑and‑forget video compressor. Drop a file, choose a target size (e.g., 8MB, 25MB, 50MB, 100MB), and let GPU-accelerated encoding produce compact outputs with AV1/HEVC/H.264. Supports NVIDIA NVENC, Intel/AMD VAAPI (Linux), and CPU fallback. The stack includes a SvelteKit UI, FastAPI backend, Celery worker, Redis broker, and real‑time progress via Server‑Sent Events (SSE).
Table of Contents
- Features
- Screenshots
- Architecture
- Installation
- Usage
- Configuration
- Reverse Proxy Configuration
- Troubleshooting
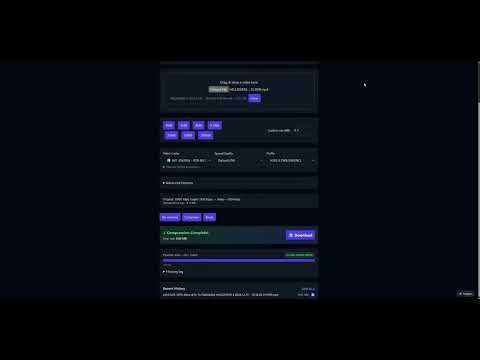
Screenshots
Main Interface
|
GPU Support List
|
Settings Panel
|
Live Queue
|
Compressing (Real-time Logs)
|
Encoder Validation Tests
|
Job History
|
Advanced Options
|
Features
- Multi-vendor GPU support: Auto-detects NVIDIA NVENC, Intel/AMD VAAPI (Linux), or falls back to CPU
- Robust encoder validation: Tests actual encoder initialization, not just availability listing
- Automatic CPU fallback: Gracefully handles missing drivers, permission issues, or hardware access problems
- Drag‑and‑drop UI with helpful presets and advanced options (codec, container, tune, audio bitrate)
- Configurable codec visibility: Enable/disable specific codecs in Settings page
- Resolution control: Set max width/height while maintaining aspect ratio
- Video trimming: Specify start/end times (seconds or HH:MM:SS format)
- ffprobe analysis on upload for instant estimates and warnings
- Real‑time progress tracking: Multi-signal progress using actual output size, time processed, bitrate, and wall-clock estimates for smooth, accurate updates
- Real‑time FFmpeg logs: Streaming logs during compression for instant feedback
- Live Queue Management: View all active jobs with real-time progress, cancel individual jobs, or clear entire queue
- One‑click Cancel: Stop an in‑flight encode; worker interrupts FFmpeg immediately
- Queue Clear: Remove all jobs (cancel running, remove queued/completed) with one click
- Automatic file size optimization: If output exceeds target by >2%, automatically re-encodes with adjusted bitrate
- Smart retry notifications: Audio alerts and visual notifications when auto-retry occurs
- History tracking enabled by default: Recent jobs stored in
/app/history.json - Auto‑download enabled by default
- Hardware encoders: AV1, HEVC (H.265), H.264 (GPU-accelerated when available)
- Software fallback: libx264, libx265, libaom-av1 for CPU-only systems
- Output container choice: MP4 or MKV, with compatibility safeguards
- Version tracking: UI displays current version (v125+), backend provides
/api/versionendpoint
Architecture (technical deep dive)
flowchart LR
A[Browser / SvelteKit UI] -- Upload / SSE --> B(FastAPI Backend)
B -- Enqueue --> C[Redis]
D[Celery Worker + FFmpeg NVENC] -- Progress / Logs --> C
B -- Pub/Sub relay --> A
D -- Files --> E[outputs/]
A -- Download --> B
Note (Nov 2025): RTX 50-Series (Blackwell) Support
🎉 RTX 50-Series Users (RTX 5090/5080/5070 Ti/etc.):
Verified working support with full NVENC hardware acceleration!Docker Image:
jms1717/8mblocal:rtx50-working
Branch:rtx50-blackwell
Complete Setup Guide: RTX50-WORKING.md⚠️ CRITICAL for RTX 50-series: You must mount the WSL driver directory:
-v /usr/lib/wsl/drivers:/usr/lib/wsl/drivers:ro
(Already configured in docker-compose.yml on the rtx50-blackwell branch)Requirements:
- RTX 50-series GPU (Blackwell/SM_100)
- NVIDIA Driver 550.x+ (tested with 581.80)
- Windows 11 WSL2 or Linux with CUDA 13 support
Verified Test Results: ✅ All 6 encoders passing (h264_nvenc, hevc_nvenc, av1_nvenc, libx264, libx265, libaom-av1)
Other NVIDIA GPUs:
- Main branch: CUDA 12.2 + FFmpeg 6.1.1, driver 535.x+ (Turing/Ampere/Ada)
- CPU/VAAPI still work if NVENC is incompatible
Intel Arc / Integrated Graphics (Linux)
Intel Arc (e.g., A140, A380) and recent Intel iGPUs are supported via VAAPI and QSV (libmfx) on Linux hosts.
- Requirements on the host:
- Linux with Intel GPU and kernel DRM i915/i915k
- Intel media driver installed on host (usually preinstalled)
- Docker with
--device /dev/driaccess
- Container configuration (already included):
- FFmpeg built with
--enable-vaapiand--enable-libmfx(QSV) - Runtime packages:
intel-media-driver,libmfx1,libva-utils - Environment:
LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=iHD
- FFmpeg built with
- How to run on Linux (bare metal):
- Uncomment the devices mapping in
docker-compose.yml:devices: ["/dev/dri:/dev/dri"]
- Uncomment the devices mapping in
Limitations:
- WSL2 (Windows) does not currently expose Intel VAAPI/QSV devices to Linux containers. On Windows, NVIDIA (CUDA/NVENC) is supported; Intel VAAPI/QSV is supported on Linux hosts.
Components
- Frontend (SvelteKit + Vite): drag‑and‑drop UI, size estimates, SSE progress/logs, final download.
- Backend API (FastAPI): accepts uploads, runs ffprobe, relays SSE, and serves downloads.
- Worker (Celery + FFmpeg 6.1.1): executes compression with auto-detected hardware acceleration (NVENC/VAAPI/CPU); parses
ffmpeg -progressand publishes updates. - Redis (broker + pub/sub): Celery broker and transport for progress/log events.
Data & files
uploads/– incoming filesoutputs/– compressed results- The backend periodically deletes old files after
FILE_RETENTION_HOURS.
Configuration
Environment Variables
WORKER_CONCURRENCY- Maximum concurrent compression jobs (default: 4, range: 1-20)BACKEND_HOST- Backend bind address (default: 0.0.0.0)BACKEND_PORT- Backend port (default: 8001)PUBLIC_BACKEND_URL- Frontend API endpoint; leave unset to use same‑origin (recommended)
Codec Visibility Settings
Control which codecs appear in the UI via environment variables or the Settings page:
CODEC_H264_NVENC,CODEC_HEVC_NVENC,CODEC_AV1_NVENC- NVIDIA encodersCODEC_H264_QSV,CODEC_HEVC_QSV,CODEC_AV1_QSV- Intel Quick SyncCODEC_H264_VAAPI,CODEC_HEVC_VAAPI,CODEC_AV1_VAAPI- AMD/Intel VAAPI (Linux)CODEC_LIBX264,CODEC_LIBX265,CODEC_LIBAOM_AV1- CPU encoders
All default to true. The system validates encoder availability at runtime and automatically falls back to CPU if hardware isn't available.
Settings UI
You can manage settings through the web interface at /settings:
- Authentication: Enable/disable auth, add/change users, change passwords
- Default Presets: Set default target size, codec, quality, container, etc.
- Codec Visibility: Enable/disable specific codecs (NVIDIA/Intel/AMD/CPU)
- GPU Support Reference: View GPU hardware encoding compatibility at
/gpu-support - No container restart required - changes take effect immediately
Example .env file:
AUTH_ENABLED=false
AUTH_USER=admin
AUTH_PASS=changeme
FILE_RETENTION_HOURS=1
WORKER_CONCURRENCY=4
REDIS_URL=redis://127.0.0.1:6379/0
BACKEND_HOST=0.0.0.0
BACKEND_PORT=8001
Using the app
- Drag & drop a video or Choose File.
- Pick a target size or enter a custom MB value, click Analyze (auto‑analyzes on drop).
Performance & Concurrency
Multiple Simultaneous Jobs
8mb.local supports running multiple compression jobs in parallel. Configure the maximum number of concurrent jobs via:
- Settings UI: Navigate to Settings → Worker Concurrency
- Environment Variable: Set
WORKER_CONCURRENCYin your.envfile (default: 4) - Docker Compose: Add
WORKER_CONCURRENCY=10to environment section
Important: Container restart required after changing concurrency setting.
Hardware-Specific Recommendations
| GPU Model | Recommended Concurrency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Quadro RTX 4000 / RTX 3060+ | 6-10 jobs | Excellent NVENC throughput, handles high concurrency well |
| RTX 3090 / 4090 | 8-12 jobs | Top-tier NVENC performance, best for bulk processing |
| GTX 1660 / RTX 2060 | 3-5 jobs | Good NVENC performance for mid-range |
| GTX 1050 Ti / Entry-level | 2-3 jobs | Basic NVENC, limited parallel capacity |
| CPU-only (libx264/libx265) | 1-2 jobs per 4 cores | Very slow, high CPU usage |
| Intel/AMD VAAPI | 4-8 jobs | Depends on iGPU/dGPU capabilities |
Performance Considerations
- NVENC Sessions: Most NVIDIA GPUs support 2-3 native NVENC sessions, but driver patches/Pro GPUs allow unlimited
- Memory Usage: Each job uses ~200-500MB RAM; monitor total system memory
- GPU Memory: Each NVENC encode uses ~100-200MB VRAM
- Disk I/O: Higher concurrency increases disk load; SSD recommended for 6+ concurrent jobs
- Thermal Throttling: Monitor GPU temps with high concurrency (>80°C may cause slowdowns)
Queue Visualization
The Queue page clearly shows which jobs are running simultaneously:
- Running jobs: Blue pulsing lightning bolt (⚡), blue border, "RUNNING NOW" indicator
- Queued jobs: Yellow "Waiting in queue" status
- Live progress: Real-time progress updates for all running jobs
Start with 4 concurrent jobs and gradually increase while monitoring GPU utilization and job completion times.
Using the app
- Drag & drop a video or Choose File.
- Pick a target size or enter a custom MB value, click Analyze (auto‑analyzes on drop).
- Optional: open Advanced Options.
- Video Codec: AV1 (best quality on newer RTX), HEVC (H.265), or H.264 (compatibility).
- Audio Codec: Opus (default) or AAC. MP4 will auto‑fallback to AAC when Opus is chosen.
- Speed/Quality: NVENC P1 (fast) … P7 (best). Default P6.
- Container: MP4 (most compatible) or MKV (best with Opus).
- Tune: Best Quality (HQ), Low Latency, Ultra‑Low Latency, or Lossless.
- Click Compress and watch progress/logs. Use Cancel to stop mid‑encode. Download starts automatically when done.
Codec/container notes
- MP4 + Opus isn’t widely supported. If MP4+Opus is selected, the worker automatically uses AAC to preserve compatibility. MKV supports Opus directly.
- MP4 outputs include
+faststartfor better web playback. - H.264/HEVC outputs are set to a compatible pixel format (yuv420p) and profiles.
Performance tips
- For very small targets, prefer AV1/HEVC and keep audio around 96–128 kbps.
- If speed matters, try Low/Ultra‑Low latency tunes with a faster preset (P1–P4). For best quality, use HQ with P6/P7.
GPU support tips
Hardware Acceleration Support
8mb.local automatically detects and uses available hardware acceleration:
NVIDIA GPU (NVENC): Best support for AV1, HEVC, H.264
- Requires RTX 40/50 series for AV1, GTX 10+ for HEVC/H.264
- Windows: Docker Desktop + WSL2 with GPU enabled; install NVIDIA drivers and Container Toolkit in WSL2
- Linux: Install NVIDIA drivers and NVIDIA Container Toolkit
- Use
--gpus allflag in docker run command - Check:
docker exec 8mblocal bash -c "ffmpeg -hide_banner -encoders | grep -i nvenc"
Intel GPU (Quick Sync Video - QSV): Good support for H.264, HEVC, AV1 (Arc GPUs)
- Requires Intel GPU with QSV support (most 6th gen+ Core CPUs and Arc GPUs)
- Linux: Ensure
/dev/driis accessible in container - Use
--device=/dev/dri:/dev/driflag in docker run command - Check:
docker exec 8mblocal bash -c "ffmpeg -hide_banner -encoders | grep -i qsv"
AMD GPU (VAAPI - Linux only): Support for H.264, HEVC, AV1
- Linux: VAAPI (requires Mesa drivers and
/dev/driaccess) - Use
--device=/dev/dri:/dev/driflag in docker run command - AMD RDNA 2+ recommended for best compatibility
- Check:
docker exec 8mblocal bash -c "ffmpeg -hide_banner -encoders | grep vaapi"
- Linux: VAAPI (requires Mesa drivers and
CPU Fallback: Works on any system without GPU
- Uses libx264 (H.264), libx265 (HEVC), libaom-av1 (AV1)
- Slower but universal compatibility
- Automatically used if hardware encoder unavailable
The system validates encoder availability at runtime and automatically falls back to CPU if hardware isn't available. You'll see log messages like:
- "Using encoder: h264_vaapi (requested: h264_vaapi)" - Hardware working
- "Warning: h264_vaapi not available, falling back to CPU (libx264)" - CPU fallback
- "Warning: hevc_nvenc failed initialization test (driver/library issue), falling back to CPU" - Hardware listed but can't initialize
Installation
Quick Start with Docker
The easiest way to run 8mb.local is with the pre-built Docker image. Choose the command for your system:
CPU Only (No GPU)
docker run -d --name 8mblocal -p 8001:8001 -v ./uploads:/app/uploads -v ./outputs:/app/outputs jms1717/8mblocal:latest
NVIDIA GPU (NVENC)
docker run -d --name 8mblocal --gpus all -e NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,video,utility -p 8001:8001 -v ./uploads:/app/uploads -v ./outputs:/app/outputs jms1717/8mblocal:latest
Note: The
-e NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,video,utilityenvironment variable is required to enable NVENC support. It tells the NVIDIA Container Toolkit to mount video encoding libraries into the container.
Intel/AMD GPU (VAAPI - Linux)
docker run -d --name 8mblocal --device=/dev/dri:/dev/dri -p 8001:8001 -v ./uploads:/app/uploads -v ./outputs:/app/outputs jms1717/8mblocal:latest
NVIDIA + VAAPI (Dual GPU - Linux)
docker run -d --name 8mblocal --gpus all -e NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,video,utility --device=/dev/dri:/dev/dri -p 8001:8001 -v ./uploads:/app/uploads -v ./outputs:/app/outputs jms1717/8mblocal:latest
Access the web UI at: http://localhost:8001
Docker Compose
For easier management, use Docker Compose. Create a docker-compose.yml file:
CPU Only
services:
8mblocal:
image: jms1717/8mblocal:latest
container_name: 8mblocal
ports:
- "8001:8001"
volumes:
- ./uploads:/app/uploads
- ./outputs:/app/outputs
- ./.env:/app/.env # Optional: for custom settings
restart: unless-stopped
NVIDIA GPU
services:
8mblocal:
image: jms1717/8mblocal:latest
container_name: 8mblocal
ports:
- "8001:8001"
volumes:
- ./uploads:/app/uploads
- ./outputs:/app/outputs
- ./.env:/app/.env # Optional: for custom settings
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,video,utility # Required for NVENC
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- driver: nvidia
count: all
capabilities: [gpu]
Intel/AMD VAAPI (Linux)
services:
8mblocal:
image: jms1717/8mblocal:latest
container_name: 8mblocal
ports:
- "8001:8001"
volumes:
- ./uploads:/app/uploads
- ./outputs:/app/outputs
- ./.env:/app/.env # Optional: for custom settings
devices:
- /dev/dri:/dev/dri
restart: unless-stopped
NVIDIA + VAAPI (Dual GPU)
services:
8mblocal:
image: jms1717/8mblocal:latest
container_name: 8mblocal
ports:
- "8001:8001"
volumes:
- ./uploads:/app/uploads
- ./outputs:/app/outputs
- ./.env:/app/.env # Optional: for custom settings
devices:
- /dev/dri:/dev/dri
restart: unless-stopped
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- driver: nvidia
count: all
capabilities: [gpu]
Then run:
docker compose up -d
Building from Source
If you want to build the image yourself:
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/JMS1717/8mb.local.git cd 8mb.localBuild and run:
docker build -t 8mblocal:local . docker run -d --name 8mblocal -p 8001:8001 -v ./uploads:/app/uploads -v ./outputs:/app/outputs 8mblocal:local
Or with Docker Compose:
docker compose up -d --build
Configuration
Create a .env file in the same directory as your docker-compose.yml (optional):
# Authentication (can also be configured via Settings UI)
AUTH_ENABLED=false
AUTH_USER=admin
AUTH_PASS=changeme
# File retention
FILE_RETENTION_HOURS=1
# Codec visibility (all default to true)
CODEC_H264_NVENC=true
CODEC_HEVC_NVENC=true
CODEC_AV1_NVENC=true
CODEC_H264_QSV=true
CODEC_HEVC_QSV=true
CODEC_AV1_QSV=true
CODEC_H264_VAAPI=true
CODEC_HEVC_VAAPI=true
CODEC_AV1_VAAPI=true
CODEC_LIBX264=true
CODEC_LIBX265=true
CODEC_LIBAOM_AV1=true
# Redis (internal, usually no need to change)
REDIS_URL=redis://127.0.0.0:6379/0
BACKEND_HOST=0.0.0.0
BACKEND_PORT=8001
Mount it with -v ./.env:/app/.env in docker run, or add it to volumes in docker-compose.yml.
Reverse Proxy Configuration
CRITICAL for Real-Time Progress: If using a reverse proxy (nginx, Nginx Proxy Manager, Traefik, etc.), SSE (Server-Sent Events) requires special configuration to prevent buffering:
Nginx / Nginx Proxy Manager
Add to your proxy configuration for the /api/stream/ location:
location /api/stream/ {
proxy_pass http://backend:8001;
proxy_buffering off; # REQUIRED - Disables response buffering for SSE
proxy_cache off; # Recommended - Disables caching
proxy_set_header Connection ''; # Recommended - Removes connection header
chunked_transfer_encoding on; # Recommended - Enables chunked transfer
}
In Nginx Proxy Manager:
- Edit your Proxy Host
- Go to "Advanced" tab
- Add to "Custom Nginx Configuration":
location /api/stream/ { proxy_buffering off; proxy_cache off; proxy_set_header Connection ''; chunked_transfer_encoding on; }
Traefik
Add labels to your docker-compose:
labels:
- "traefik.http.middlewares.no-buffer.buffering.maxRequestBodyBytes=0"
- "traefik.http.middlewares.no-buffer.buffering.maxResponseBodyBytes=0"
- "traefik.http.routers.8mblocal.middlewares=no-buffer"
Apache
<Location /api/stream/>
ProxyPass http://backend:8001/api/stream/
ProxyPassReverse http://backend:8001/api/stream/
SetEnv proxy-sendchunked 1
SetEnv proxy-interim-response RFC
</Location>
Why this matters: Without proxy_buffering off, nginx buffers the entire SSE response and sends all progress events at once when the job completes, instead of streaming them in real-time. You'll see "progress stuck at 0%" until completion, then everything updates instantly.
Testing: After configuring, start a compression job. You should see:
- Progress bar updating smoothly in real-time
- FFmpeg logs appearing as encoding happens
- Browser console showing SSE events:
SSE connection opened,SSE event: progress
If progress still doesn't update until completion, check your proxy logs and verify proxy_buffering off; is applied.
Platform-Specific Setup
Windows
- Install Docker Desktop
- For NVIDIA GPU: Install NVIDIA drivers, enable WSL2 GPU support in Docker Desktop settings
- Use the NVIDIA GPU docker command above
- Note: AMD GPUs don't work in Docker on Windows (VAAPI is Linux-only)
Linux
- Install Docker:
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | sh - For NVIDIA: Install NVIDIA drivers and NVIDIA Container Toolkit
- For Intel/AMD: Ensure
/dev/driexists and user has access (ls -l /dev/dri) - Add your user to docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER(logout/login required) - Use the appropriate docker command for your GPU
macOS
- Install Docker Desktop
- Note: No GPU acceleration available on macOS (Docker runs in Linux VM without GPU passthrough)
- Use CPU-only docker command
- Performance will be slower but functional
Verify Installation
Check container is running:
docker ps | grep 8mblocalCheck available encoders:
docker exec 8mblocal bash -c "ffmpeg -hide_banner -encoders | grep -E 'nvenc|qsv|vaapi|264|265|av1'"View logs:
docker logs 8mblocal
Access the UI at http://localhost:8001 and go to Settings → Available Codecs to see detected hardware.
Update to Latest Version
Pull the latest image and restart:
docker pull jms1717/8mblocal:latest
docker stop 8mblocal
docker rm 8mblocal
# Then run your docker run command again, or:
docker compose pull
docker compose up -d
Troubleshooting
Container won't start on a system without NVIDIA GPU
If you run with --gpus all (or have gpus: all in compose) on a host with no NVIDIA adapter, Docker's NVIDIA prestart hook will abort before our app starts:
nvidia-container-cli: initialization error: WSL environment detected but no adapters were found
Fix: remove --gpus all and any NVIDIA_* environment variables. The app will start in CPU mode automatically. For Intel/AMD on Linux, use /dev/dri mapping instead (see Intel/AMD sections above).
Hardware Acceleration Issues
NVENC "Operation not permitted" or "Driver does not support required nvenc API version" error:
Most common cause: Missing
NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIESenvironment variableSolution: Add
-e NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,video,utilityto your docker run commandExample:
docker run -d --name 8mblocal \ --gpus all \ -e NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,video,utility \ -p 8001:8001 \ -v ./uploads:/app/uploads \ -v ./outputs:/app/outputs \ jms1717/8mblocal:latestThis tells the NVIDIA Container Toolkit to mount NVENC libraries into the container
Critical: Driver Version Mismatch - The #1 cause of NVENC failures:
- Error symptom:
Driver does not support the required nvenc API version. Required: 13.0 Found: 12.1 - Root cause: Container ffmpeg requires NVENC API 13.0, but host driver only provides 12.1
- Who's affected: Systems running NVIDIA driver 535.x (common on Debian 12 stable, older Ubuntu LTS)
- Quick check: Run
nvidia-smiand look at driver version:- Driver 535.x = NVENC API 12.1 ❌ (too old)
- Driver 550.x or newer = NVENC API 13.0 ✅ (compatible)
- Error symptom:
Solution: Upgrade NVIDIA Driver
For Debian 12 systems:
# Debian backports has older drivers - use NVIDIA's official repo instead wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/debian12/x86_64/cuda-keyring_1.1-1_all.deb sudo dpkg -i cuda-keyring_1.1-1_all.deb sudo apt update sudo apt install nvidia-driver sudo reboot # Required to load new driverFor Ubuntu systems:
# Add NVIDIA PPA for latest drivers sudo add-apt-repository ppa:graphics-drivers/ppa sudo apt update sudo apt install nvidia-driver-550 # or newer sudo rebootAfter reboot, verify:
nvidia-smishould show driver 550+ andffmpeg -encoders | grep nvencinside container should work.Why this happens: Newer ffmpeg builds use NVENC API 13.0 features for better quality/performance. Older drivers (535.x) only support up to API 12.1.
Verification steps:
- Check host driver:
nvidia-smi(look for version 550+) - Test NVENC in container:
docker exec 8mblocal ffmpeg -f lavfi -i nullsrc -c:v h264_nvenc -f null - - If you see "Cannot load libnvidia-encode.so.1", add the
NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIESenv var above - If you see "Required: 13.0 Found: 12.1", upgrade your driver
- Check host driver:
On Linux: Verify NVIDIA Container Toolkit is installed
If driver upgrade not possible: System will automatically fallback to CPU encoding
Intel QSV not working:
- Ensure
/dev/driexists:ls -l /dev/dri - Check device permissions:
groupsshould showvideoorrender - Verify
--device=/dev/dri:/dev/driflag is used - Install Intel GPU drivers if needed
- Ensure
AMD VAAPI issues:
- Ensure Mesa drivers installed:
glxinfo | grep -i mesa(installmesa-utils) - Check
/dev/driexists and is accessible - Verify
--device=/dev/dri:/dev/driflag is used - AMD RDNA 2+ recommended for best AV1 support
- VAAPI device errors ("No VA display found"): System will automatically fall back to CPU
- Ensure Mesa drivers installed:
System automatically falls back to CPU
- This is expected behavior if hardware encoder isn't available
- Check Settings → Available Codecs to see what's enabled
- Look for log messages: "Warning: X not available, falling back to CPU (Y)"
- CPU encoding works but is slower - consider enabling fewer codecs or using faster presets
NVENC "Operation not permitted" Error
This error occurs when NVENC encoder fails to initialize. The system now automatically detects this and falls back to CPU, but if you want GPU acceleration:
Error Messages You May See:
"Cannot load libnvidia-encode.so.1"
- Cause: Missing
NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIESenvironment variable - Fix: Add
-e NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,video,utilityto docker run command (see example in NVENC section above) - Why: By default, NVIDIA Container Toolkit only mounts compute libraries, not video encoding libraries
- Cause: Missing
"Driver does not support the required nvenc API version. Required: 13.0 Found: 12.1"
- Cause: Your NVIDIA driver is too old (535.x series only supports NVENC API 12.1)
- Fix: Upgrade to driver 550+ using the instructions in the NVENC troubleshooting section above
- Common on: Debian 12 stable, older Ubuntu LTS releases
- Verification: Run
nvidia-smiand check driver version
"Could not open encoder before EOF" or "Task finished with error code: -22 (Invalid argument)"
- Cause: Usually accompanies one of the errors above
- Effect: FFmpeg crashes with exit code 255
- Fix: Resolve the underlying library or API version issue
Common causes:
- Driver API version mismatch (most common - see error #2 above)
- Missing video encoding libraries (see error #1 above)
- Missing NVIDIA Container Toolkit: Docker can't access GPU
- Insufficient permissions: Container can't access encoder
Quick Fix (Automatic): The system will detect the initialization failure and automatically use CPU encoding. You'll see:
Warning: hevc_nvenc failed initialization test (driver/library issue), falling back to CPU
Using encoder: libx265 (requested: hevc_nvenc)
Your video will still compress, just using CPU instead of GPU.
To Enable GPU (Optional):
Fix missing NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES (if you saw error #1 above):
- Add environment variable to docker run:
-e NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,video,utility - Or in Docker Compose:
environment: - NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=compute,video,utility
- Add environment variable to docker run:
Upgrade NVIDIA driver (if you saw error #2 above):
- See detailed upgrade instructions in the "NVENC issues" section above
- Debian 12: Use NVIDIA's official CUDA repository (not backports)
- Ubuntu: Use graphics-drivers PPA
- Requires reboot after installation
Missing NVIDIA Container Toolkit: Docker can't access GPU
- Install:
distribution=$(. /etc/os-release;echo $ID$VERSION_ID) && curl -fsSL https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/gpgkey | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/nvidia-container-toolkit-keyring.gpg && curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/$distribution/libnvidia-container.list | sed 's#deb https://#deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nvidia-container-toolkit-keyring.gpg] https://#g' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-container-toolkit.list && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y nvidia-container-toolkit - Restart Docker:
sudo systemctl restart docker
- Install:
Workaround if upgrade not possible: Disable NVENC and use CPU or VAAPI
- Go to Settings → Available Codecs
- Uncheck all NVENC codecs (H.264/HEVC/AV1)
- Enable CPU codecs or VAAPI if you have Intel/AMD GPU
- System will automatically use available encoders
Real-World Example: Debian 12 with Driver 535 On a fresh Debian 12 install with Quadro RTX 4000, the default driver (535.247.01) is too old:
# Initial state - fails with API 12.1 vs 13.0 error
nvidia-smi # Shows driver 535.247.01
# Fix by upgrading to NVIDIA's official driver repository
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/debian12/x86_64/cuda-keyring_1.1-1_all.deb
sudo dpkg -i cuda-keyring_1.1-1_all.deb
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nvidia-driver # Installs 550+ series
sudo reboot
# After reboot - NVENC works!
nvidia-smi # Shows driver 580.95.05 or newer
This resolved the exact issue encountered on the powerhouse server.
General Issues
Permission denied writing uploads/outputs:
- Ensure directories exist and have correct permissions
- Try:
chmod 777 uploads outputsorchown -R $USER:$USER uploads outputs
Ports in use:
- Change port mapping:
-p 8080:8001instead of-p 8001:8001 - Usually no need to set
PUBLIC_BACKEND_URL(frontend uses same‑origin)
- Change port mapping:
Progress bar stuck at 0% until job completes:
- Cause: Reverse proxy (nginx/NPM/Traefik) is buffering SSE responses
- Symptom: All progress events arrive at once when encoding finishes
- Fix: Add
proxy_buffering off;to your proxy config for/api/stream/location (see Reverse Proxy Configuration section above) - Test: Check browser console for SSE events during encoding, not just at completion
Container won't start:
- Check logs:
docker logs 8mblocal - Verify .env file syntax if using custom configuration
- Try removing container and running again:
docker rm -f 8mblocal
- Check logs:
Files slightly over target size:
- Expected behavior: System automatically retries if >2% over target
- You'll see a notification: "File exceeded target by X.X%, retrying with adjusted bitrate"
- Sound alert plays when retry occurs
- Check logs for "Retry attempt" messages
FFmpeg errors:
- Full command and last 20 lines of stderr are logged for debugging
- Check Settings → Available Codecs to ensure correct encoders enabled
- Try CPU fallback: enable only libx264/libx265/libaom-av1
Getting Help
- Check the logs:
docker logs 8mblocal - View ffmpeg command in UI logs during compression
- Visit Settings → GPU Support for hardware compatibility reference
- Verify GPU access:
docker exec 8mblocal nvidia-smi(NVIDIA) ordocker exec 8mblocal ls -l /dev/dri(VAAPI) - Check available encoders:
docker exec 8mblocal bash -c "ffmpeg -hide_banner -encoders | grep -E 'nvenc|qsv|vaapi|264|265|av1'" - Open an issue on GitHub with logs and system details
Quick Troubleshooting Commands
# Check if container is running
docker ps | grep 8mblocal
# View container logs
docker logs 8mblocal
# Check NVIDIA GPU status (if using NVENC)
docker exec 8mblocal nvidia-smi
# Check available video devices (if using VAAPI)
docker exec 8mblocal ls -l /dev/dri
# List available encoders in container
docker exec 8mblocal bash -c "ffmpeg -hide_banner -encoders | grep -E 'nvenc|qsv|vaapi|264|265|av1'"
# Check NVIDIA libraries (if using NVENC)
docker exec 8mblocal bash -c "ls -l /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnvidia-encode.so*"
# Restart container
docker restart 8mblocal
# View real-time logs
docker logs -f 8mblocal
Notes
- Hardware acceleration is automatically detected and validated at runtime
- System automatically falls back to CPU encoding if hardware encoder unavailable
- Automatic file size optimization: Files >2% over target are automatically re-encoded with adjusted bitrate
- Real-time progress tracking: SSE streams progress updates to both main and queue pages
- Reverse proxy configuration required: nginx/NPM users must add
proxy_buffering off;for/api/stream/(see Reverse Proxy Configuration section) - AV1 support varies by hardware: NVIDIA (RTX 40/50-series), Intel (Arc GPUs), AMD (RDNA 3+), or CPU fallback
- MP4 + Opus is not supported; the worker auto‑encodes AAC in MP4 containers
- Configure codec visibility in Settings → Available Codecs or via environment variables
- All components (Redis, Backend, Worker, Frontend) run in a single container via supervisord
- Consider HTTPS termination and stronger auth for public deployments
License
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
You are free to use, share, and adapt this project for non-commercial purposes as long as you provide appropriate attribution.
You are not allowed to use this project for commercial purposes under this license.
Looking to use this project commercially? I offer a separate commercial license that grants you the right to use this project in your commercial products.
Please contact me directly.
Contributing
Pull requests welcome! Please ensure Docker builds succeed and test with your GPU hardware.
Support
For issues, questions, or feature requests, please open an issue on GitHub.